What is Factorize 2?
This activity allows the user to find all of the factorizations of a given number and then draw the product as the area of a rectangle on a grid. Users can choose to enter in their own numbers and can also receive hints if they are having trouble.
Factors are numbers that when multiplied together form a unique product. For example, 2 factors of 15 are 3 and 5 because 3 * 5 = 15. Every number has at least 2 factors, 1 and the number since 1 multiplied by any number is itself (though when finding the factors of 1, those two are the same number).
A number that only has two factors, one and itself, is called a prime number. However, some numbers have many factors. For example, the factors of 24 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12, and 24.
How Do I Use This Activity?
This activity allows the user to visually explore the concept of factors by creating rectangular arrays on a grid whose area is equal to the product of the factors.
Controls and Output
-
A number between 0 and 50 is randomly selected. The user can either determine the factors
of that number, randomly select another number by using the
Get New # button, or specify a number by inputting a number next to the
UseThis # button and then clicking the button.

-
Choose whether or not you wish the applet to use the commutative property by either
clicking on the "Show Commutative property" or "Do not show Commutative property" bubble.

- If you choose "Do not show Commutative property" then you do not need to enter the expression b x a if you've entered a x b.
- If you choose "Show Commutative property" then you need to enter both forms of the expression: a x b and b x a.
-
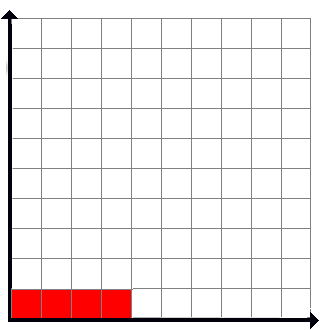
Click and drag across the grid to color a rectangle with the dimensions of a factorization whose area (i.e. product) is equal to the number shown. The resulting rectangle must have the same area as the product of the factors.
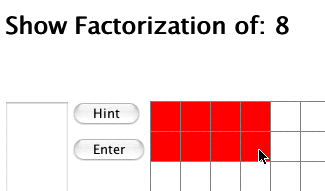
Note: If you chose "Show commutative property", when drawing the rectangle with the dimensions of the factors, imagine the grid as if it were the first quadrant of the coordinate plane and your factors as your x-axis and y-axis movements. For example: 4 * 1 would be displayed as 4 over and 1 up. 4 is your x-axis movement and 1 is your y-axis movement. Your drawing will be counted as 1 * 4 otherwise!
- After you have drawn the appropriate sized rectangle, click the enter button to see if the rectangle is correct.
Scoring
-
This activity will automatically record how successful you are at answering the questions.
To view the score, press the
Show Score button at the bottom of the activity and a pop-up window will appear with the scoreboard.
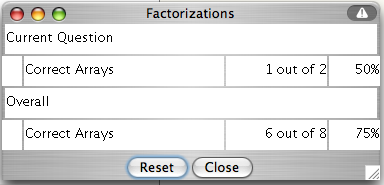 To close this pop-up window press the
Close button or click back on the main window.
To close this pop-up window press the
Close button or click back on the main window.
- To pause the scoring, press the Active button at the bottom of the screen and it will change to a Paused button. To resume scoring, press the Paused button.
- To reset the scoreboard, open the scoreboard using the Show Score button and then press the Reset button.
Description
This activity allows the user to find all of the factorizations of a given number and then visually plot them on a grid. Users can choose to enter in their own numbers and can also receive hints if they are having trouble. This activity would work well in groups of 2 for about 25 minutes if you use the exploration questions and 15 minutes otherwise.
Place in Mathematics Curriculum
This activity can be used to:
- Teach students about factors
- Visually show how factorizations make up various numbers
Standards Addressed
Grade 3
-
Functions and Relationships
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of functions.
- The student demonstrates algebraic thinking.
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates an understanding of geometric relationships.
- The student solves problems using perimeter or area.
-
Numeration
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of whole numbers up to one thousand.
Grade 4
-
Functions and Relationships
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of functions, patterns, or sequences.
- The student demonstrates algebraic thinking.
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates an understanding of geometric relationships.
- The student solves problems using perimeter or area.
-
Numeration
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of whole numbers to ten thousands.
Grade 5
-
Functions and Relationships
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of functions, patterns, or sequences.
- The student demonstrates algebraic thinking.
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates an understanding of geometric relationships.
- The student solves problems (including real-world situations) using perimeter or area.
-
Numeration
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of whole numbers to millions.
Grade 6
-
Estimation and Computation
- The student accurately solves problems (including real-world situations).
-
Numeration
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of fractions (proper or mixed numbers), decimals, percents (whole number), or integers.
Grade 7
-
Estimation and Computation
- The student accurately solves problems (including real-world situations).
Grade 8
-
Estimation and Computation
- The student accurately solves problems (including real-world situations).
Grade 9
-
Estimation and Computation
- The student accurately solves problems (including real-world situations).
-
Numeration
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of real numbers.
Grade 10
-
Estimation and Computation
- The student accurately solves problems (including real-world situations).
-
Numeration
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of real numbers.
Grade 4
-
Number Sense
- 4.0 Students know how to factor small whole numbers
Third Grade
-
Measurement and Data
- Geometric measurement: understand concepts of area and relate area to multiplication and to addition.
-
Operations and Algebraic Thinking
- Represent and solve problems involving multiplication and division.
- Understand properties of multiplication and the relationship between multiplication and division.
- Multiply and divide within 100.
Fourth Grade
-
Operations and Algebraic Thinking
- Use the four operations with whole numbers to solve problems.
- Gain familiarity with factors and multiples.
Sixth Grade
-
The Number System
- Compute fluently with multi-digit numbers and find common factors and multiples.
Algebra
-
Arithmetic with Polynomials and Rational Expressions
- Use polynomial identities to solve problems
Grades 6-8
-
Numbers and Operations
- Understand meanings of operations and how they relate to one another
Grade 4
-
Number and Operations, Measurement, Geometry, Data Analysis and Probability, Algebra
- COMPETENCY GOAL 1: The learner will read, write, model, and compute with non-negative rational numbers.
- COMPETENCY GOAL 2: The learner will understand and use perimeter and area.
6th Grade
-
Algebra
- The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of writing, interpreting, and using mathematical expressions, equations, and inequalities.
-
Numbers and Operations
- The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of the concepts of whole-number percentages, integers, and ratio and rate; the addition and subtraction of fractions; accurate, efficient, and generalizable methods of multiplying and dividing fractions and decimals; and the use of exponential notation to represent whole numbers.
5th Grade
-
Algebra
- The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of the use of patterns, relations, functions, models, structures, and algebraic symbols to represent quantitative relationships and will analyze change in various contexts.
8th Grade
-
Algebra
- The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of equations, inequalities, and linear functions.
Elementary Algebra
-
Elementary Algebra
- Standard EA-2: The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of the real number system and operations involving exponents, matrices, and algebraic expressions.
Intermediate Algebra
-
Algebra
- The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of quadratic equations and the complex number system.
7th Grade
-
Number and Number Sense
- 7.3 The student will identify and apply the following properties of operations with real numbers: the commutative and associative properties for addition and multiplication; the distributive property; the additive and multiplicative identity properties; the additive and multiplicative inverse properties; and the multiplicative property of zero.
Textbooks Aligned
Grade Six
-
Prime Time
- Investigation One: The Factor Game
- Investigation Three: Factor Pairs
- Investigation Five: Factorizations
Book 1
-
Module 4 - Mind Games
- Section 2: Prime Factors
Book 2
-
Module 3 - A Universal Language
- Section 1: Prime Factorization
- Section 1: Common Factors
- Section 1: Common Multiples
6th
-
Module 3 - Mind Games
- Section 3: Factors and Divisibility
Book 1
-
Patterns in Numbers and Shapes
- Lesson 3: Crossing the River
Book 2
-
Making Mathematical Arguments
- Lesson 10: A Stretching Problem
Grade 8
-
Reflections on Number
- Divisibility and Prime Factorization
- Multiplication and Division
- Operations with Inverses
Grade 6
-
Operations
- Operations with Integers
- Plotting Points
- Coordinate Plane
Be Prepared to
- Encourage students to enter in numbers that have many factors such as 12 or 24
- Show students how to build the factorizations by dragging the mouse over the desired area