What is Floor Tiles?
This activity allows the user to generate a quadrilateral that will repeat without overlapping across a plane. Starting from a rectangle, the user moves the corners of the quadrilateral, creating a new four-sided figure. The user can choose several different colors to enhance the pattern, and can observe the different effects that colors have on tessellations.
If we start from a rectangle,
then select colors for the shape,
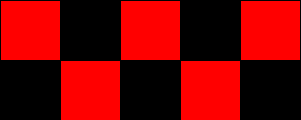
clicking on the Tessellate button results in a plane covered with repetitions of the quadrilateral with no overlapping or gaps in between the shapes.
Dragging the corners of the original rectangle to form an irregular quadrilateral
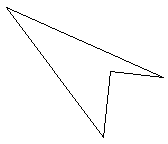
and selecting colors for the shapes renders this image:

Tessellations occur naturally in the world, and are frequently used in designs for works of art and architecture. They can assist students in conceptualizing infinity, learning about the different types of symmetry, and making observations about how colors and shapes affect perception.
How Do I Use This Activity?
This activity allows the user to create a figure that can be tessellated.
Controls and Output
Located in the middle of the applet screen is a quadrilateral.
 The user can alter the shape of the quadrilateral by clicking on any corner of it and
dragging it to the desired location.
The user can alter the shape of the quadrilateral by clicking on any corner of it and
dragging it to the desired location.
 Along the bottom of the applet is set of controls that allow the user to specify information
about the tessellation.
Along the bottom of the applet is set of controls that allow the user to specify information
about the tessellation.
-
Clicking on the
Reset button will reset the quadrilateral to its original form.

-
Clicking on the
Tessellate button will fill the drawing area with tessellated copies of the shape. Once a shape is
tessellated, clicking on the
Edit button will remove all of the tessellated copies and allow the user to continue editing
the shape.
-
The button labeled
Information will bring up a list of information about the shape, including its area, perimeter, and
the Cartesian coordinates of its vertices.

-
The row of list boxes along the bottom allows the user to select which colors the shape
will be drawn in when it is tessellated. Setting both of these boxes to White will draw
the tessellation without color.
Description
This activity allows the user to explore the world of tessellations on quadrilateral figures by dynamically changing the shape of the quadrilateral through dragging corners. This activity would work well in mixed ability groups of two or three for about twenty minutes if you use the exploration questions and ten to fifteen minutes otherwise.
Place in Mathematics Curriculum
This activity can be used to:
- recognize and explore the properties of tessellations
- identify and examine symmetry in geometric figures
- describe, and classify polygons
- examine the role of mathematics in society and nature
Standards Addressed
Grade 3
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates an understanding of geometric relationships.
- The student demonstrates understanding of position and direction.
- The student demonstrates a conceptual understanding of geometric drawings or constructions.
Grade 4
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates an understanding of geometric relationships.
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of similarity, congruence, symmetry, or transformations of shapes.
- The student demonstrates understanding of position and direction.
- The student demonstrates a conceptual understanding of geometric drawings or constructions.
Grade 5
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates an understanding of geometric relationships.
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of similarity, congruence, symmetry, or transformations of shapes.
- The student demonstrates understanding of position and direction.
- The student demonstrates a conceptual understanding of geometric drawings or constructions.
Grade 6
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates an understanding of geometric relationships.
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of similarity, congruence, symmetry, or transformations of shapes.
- The student demonstrates a conceptual understanding of geometric drawings or constructions.
Grade 7
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates an understanding of geometric relationships.
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of similarity, congruence, symmetry, or transformations of shapes.
- The student demonstrates a conceptual understanding of geometric drawings or constructions.
Grade 8
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates an understanding of geometric relationships.
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of similarity, congruence, symmetry, or transformations of shapes.
- The student demonstrates a conceptual understanding of geometric drawings or constructions.
Grade 9
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates an understanding of geometric relationships.
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of similarity, congruence, symmetry, or transformations of shapes.
- The student demonstrates a conceptual understanding of geometric drawings or constructions.
Grade 10
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates an understanding of geometric relationships.
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of similarity, congruence, symmetry, or transformations of shapes.
- The student demonstrates a conceptual understanding of geometric drawings or constructions.
Third Grade
-
Geometry
- Reason with shapes and their attributes.
Fourth Grade
-
Operations and Algebraic Thinking
- Generate and analyze patterns.
Fifth Grade
-
Operations and Algebraic Thinking
- Analyze patterns and relationships.
Geometry
-
Congruence
- Experiment with transformations in the plane
- Understand congruence in terms of rigid motions
Grades 3-5
-
Geometry
- Apply transformations and use symmetry to analyze mathematical situations
- Use visualization, spatial reasoning, and geometric modeling to solve problems
Grades 6-8
-
Geometry
- Apply transformations and use symmetry to analyze mathematical situations
- Use visualization, spatial reasoning, and geometric modeling to solve problems
Grades 9-12
-
Geometry
- Analyze characteristics and properties of two- and three-dimensional geometric shapes and develop mathematical arguments about geometric relationships
- Use visualization, spatial reasoning, and geometric modeling to solve problems
Grade 5
-
Number and Operations, Measurement, Geometry, Data Analysis and Probability, Algebra
- COMPETENCY GOAL 3: The learner will understand and use properties and relationships of plane figures.
Geometry
-
Geometry and Measurement
- Competency Goal 2: The learner will use geometric and algebraic properties of figures to solve problems and write proofs.
Technical Mathematics I
-
Geometry and Measurement
- Competency Goal 2: The learner will measure and apply geometric concepts to solve problems.
Technical Mathematics II
-
Geometry and Measurement
- Competency Goal 1: The learner will use properties of geometric figures to solve problems.
Integrated Mathematics III
-
Geometry and Measurement
- Competency Goal 2: The learner will use properties of geometric figures to solve problems.
5th Grade
-
Geometry
- The student will develop an understanding of geometric concepts and relationships as the basis for geometric modeling and reasoning to solve problems involving one-, two-, and three-dimensional figures.
3rd Grade
-
Geometry
- Content Standard 3.0 The student will develop an understanding of geometric concepts and relationships as the basis for geometric modeling and reasoning to solve problems involving one-, two-, and three-dimensional figures.
4th Grade
-
Geometry
- The student will develop an understanding of geometric concepts and relationships as the basis for geometric modeling and reasoning to solve problems involving one-, two-, and three-dimensional figures.
Grade 4
-
Geometry and Spatial Reasoning
- 9. The student connects transformations to congruence and symmetry.
Grade 5
-
Geometry and Spatial Reasoning
- 8. The student models transformations.
Grade 8
-
Geometry and Spatial Reasoning
- 6. The student uses transformational geometry to develop spatial sense.