What is Surface Area and Volume?
This activity allows the user to manipulate three-dimensional polyhedra to experiment with surface area and volume.
Figures in three dimensions have length, depth (also often called width), and height, as we know. These three dimensions can be used to determine the volume (space taken up by) and surface area (sum of the areas of all of the faces or surfaces of the object).
Rectangular and triangular prisms are particularly easy to work with, since their faces (sides) are shapes that have areas and side lengths that can easily be measured.
This activity uses the following dimensions for rectangular prisms:
Width - When increased the rectangular prism will expand left and right so that it is wider.
Depth - When increased the rectangular prism will expand in deepness so that it looks like it is more 3D.
Height - When increased the rectangular prism will expand in length up and down so that it will become taller.
This activity uses the following dimensions for triangular prisms:
Base Width - When increased the triangular prism's rectangular base will expand left and right so that it is wider.
Prism Height - When increased the rectangular sections of the triangular prism will expand in length so that the prism appears taller.
Base Depth - When increased the distance between the base of the triangle and the apex (peak of the triangle) will expand so that the triangle height increases.
How Do I Use This Activity?
This activity allows the user to manipulate three-dimensional polyhedrons to experiment with surface area and volume.
Controls and Output
Find help for...
| Rectangular Prism | Triangular Prism |
-
To select a rectangular prism click on the drop-down box located at the bottom right side of
the screen and choose "Rectangular Prism."
-
A check box titled
Draw grid is located at the top left of the screen. When this box is checked, a grid will appear on
the polyhedron. This feature may make it easier for the user to visualize the width, depth,
and height of the polyhedron.

-
A check box titled
Draw back faces is located at the top of the screen. When this box is checked, while looking at an outlined
polyhedron with the
Draw grid box unchecked, it enables the user to visualize the polyhedron as a whole.
-
The user may choose to view the polyhedron as a filled solid or as a hollow prism by
selecting
Filled polyhedron or
Outlined polyhedron from the drop down box located at the top of the screen.
-
The
Mode box located at the top right side of the screen allows the user to select
Explore Mode or
Compute Mode.
-
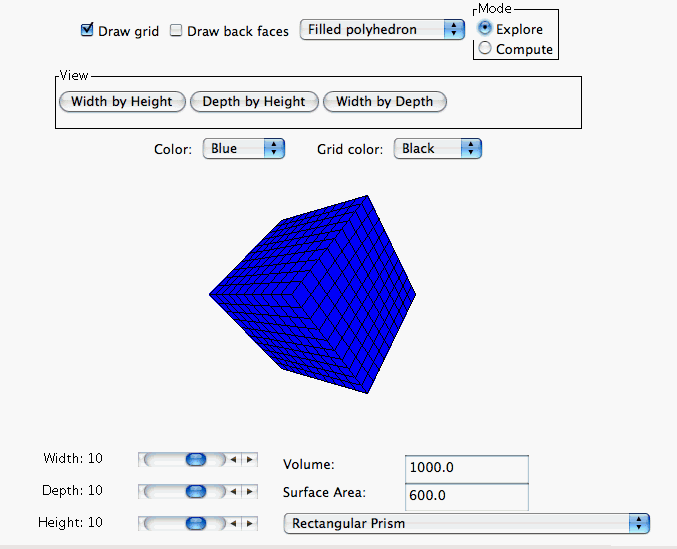
When operating in the
Explore Mode the computer automatically calculates and displays the surface area and volume of the
rectangular polyhedron. This allows the user to see what effect altering width, depth,
and height have on the surface area and volume of the polyhedron. The surface area and
volume of the polyhedron are displayed in the corresponding boxes located in the bottom
right corner of the page.
-
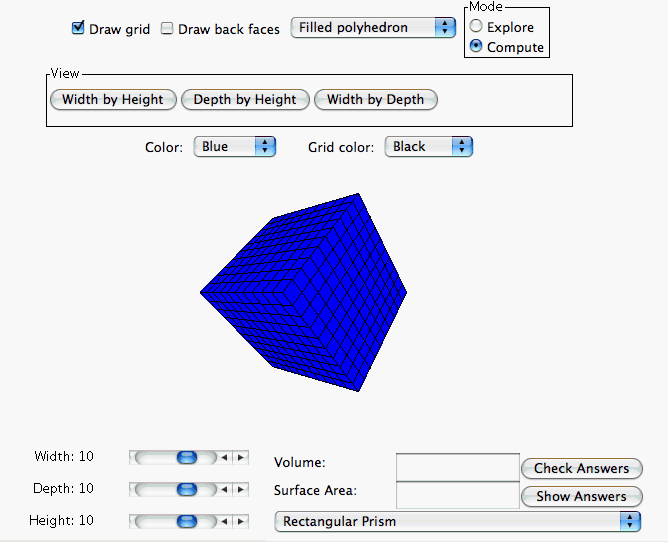
When operating in the
Compute Mode the computer hides the surface area and volume of the rectangular polyhedron. This
allows the user to calculate the surface area and volume of the polyhedron on their own.
The user can have the computer check their answers by entering their answers into the
corresponding box located at the bottom right corner of the page and clicking the
Check Answers button. Answers are considered correct if within one-tenth of the computer calculated
answer. If the user is unable to calculate the correct surface area and volume of the
polyhedron on their own they may click the
Show Answers button and the computer will display the correct answers.
-
When operating in the
Explore Mode the computer automatically calculates and displays the surface area and volume of the
rectangular polyhedron. This allows the user to see what effect altering width, depth,
and height have on the surface area and volume of the polyhedron. The surface area and
volume of the polyhedron are displayed in the corresponding boxes located in the bottom
right corner of the page.
-
The user can change the direction they are viewing the polyhedron by pressing the
Width by Height, Depth by Height, or
Width by Depth buttons located in the view box.
- The view may also be changed by placing the cursor on the polyhedron, clicking, and moving the cursor in the direction which the user would like the object to rotate.
-
Both the color of the prism and the grid line color may be changed by clicking on the
corresponding drop-down boxes located below the view box.
-
The user may increase or decrease the width, depth, or height of the polyhedron by adjusting
the appropriate scrollbar.
-
To select a triangular prism click on the drop-down box located at the bottom right side of
the screen and choose "Triangular Prism."

-
A check box titled
Draw grid is located at the top left of the screen. When this box is checked, a grid will appear on
the triangular polyhedron. This feature may make it easier for the user to visualize the
width, depth, and height of the polyhedron.

-
A check box titled
Draw back faces is located at the top of the screen. When this box is checked, while looking at an outlined
polyhedron with the
Draw grid box unchecked, it enagles the user to visualize the polyhedron as a whole.
-
The user may choose to view the polyhedron as a filled solid or as a hollow prism by
selecting
Filled polyhedron or
Outlined polyhedron from the drop down box located at the top of the screen.

-
The
Mode box located at the top right side of the screen allows the user to select
Explore Mode or
Compute Mode.

-
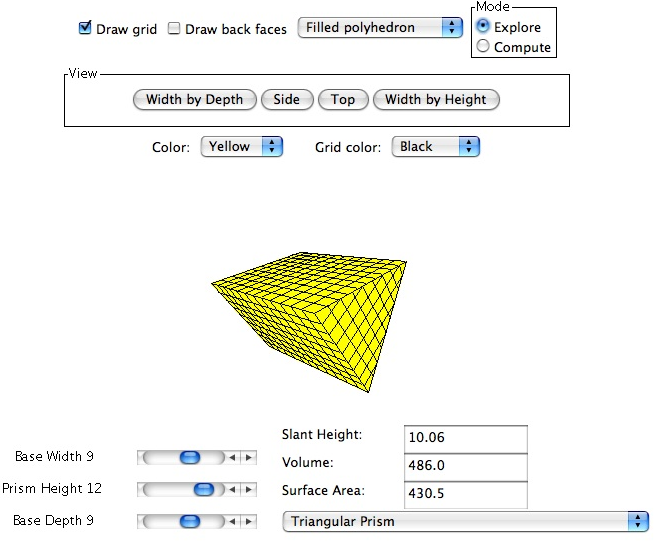
When operating in the
Explore Mode the computer automatically calculates and displays the slant height, surface area, and
volume of the triangular prism. This allows the user to see what effect altering base
width, base depth, and prism height has on the slant height, surface area, and volume of
the polyhedron. The slant height, surface area, and volume of the triangular prism are
displayed in the corresponding boxes located in the bottom right corner of the page.
-
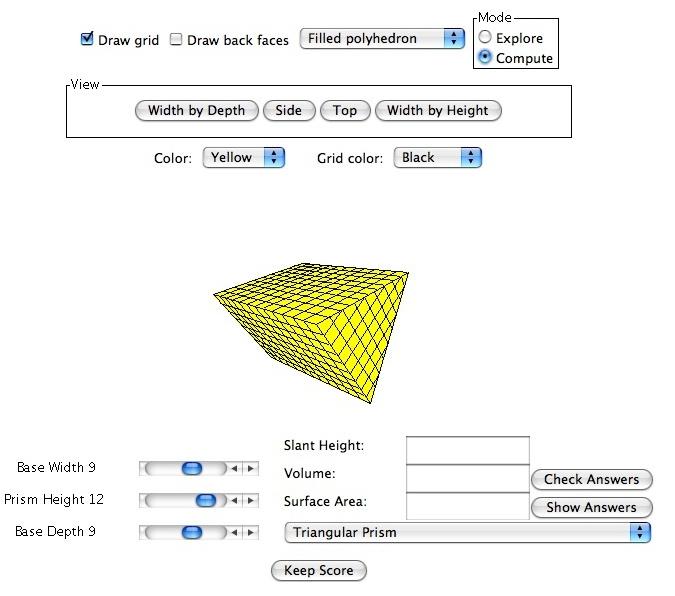
When operating in the
Compute Mode the computer hides the slant height, surface area, and volume of the triangular prism.
This allows the user to calculate the slant height, surface area, and volume of the
triangular prism on their own. The user can have the computer check their answers by
entering their answers into the corresponding box located at the bottom right corner of
the page and clicking the
Check Answers button. Answers are considered correct if within one-tenth above or below the computer
generated answer. If the user is unable to calculate the correct slant height, surface
area, and volume of the triangular prism on their own, they may click the
Show Answers button and the computer will display the correct answers.
-
When operating in the
Explore Mode the computer automatically calculates and displays the slant height, surface area, and
volume of the triangular prism. This allows the user to see what effect altering base
width, base depth, and prism height has on the slant height, surface area, and volume of
the polyhedron. The slant height, surface area, and volume of the triangular prism are
displayed in the corresponding boxes located in the bottom right corner of the page.
-
Definitions
- The base of the triangular prism is the triangular end of the prism.
- The height of the triangular prism is the distance between the two bases.
- The width of the triangular prism is the length of the base of the triangle.
- The base depth of the triangular prism is the perpendicular distance fromt he base of the triangle to the top of the triangle.
-
The user can change the direction they are viewing the polyhedron by pressing the
Width by Height, Side, Top, or
Width by Depth buttons located in the view box.
- The view may also be changed by placing the cursor on the polyhedron, clicking, and moving the cursor in the direction which the user would like the object to rotate.
-
Both the color of the prism and the grid line color may be changed by clicking on the
corresponding drop-down boxes located below the view box.
-
The user may increase or decrease the width, depth, or height of the polyhedron by adjusting
the appropriate scrollbar.

Because this activity randomly generates questions, a feature called Seed Random has been implemented that allows multiple users using different computers to work on the same problem. See Seed Random Help for instructions on using this feature.
Description
This activity allows the user to manipulate three-dimensional polyhedrons to experiment with surface area and volume.
This activity would work well in groups of 2 for about 25-30 minutes if you use the exploration questions and 15-20 minutes otherwise.
Place in Mathematics Curriculum
This activity can be used to:
- illustrate notions of surface area and volume
- develop students visualization skills
- practice students skills at estimating surface area and volume
Standards Addressed
Grade 6
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates an understanding of geometric relationships.
- The student solves problems (including real-world situations) using perimeter, area, or volume.
- The student demonstrates a conceptual understanding of geometric drawings or constructions.
Grade 7
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates an understanding of geometric relationships.
- The student solves problems (including real-world situations).
- The student demonstrates a conceptual understanding of geometric drawings or constructions.
Grade 8
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates an understanding of geometric relationships.
- The student solves problems (including real-world situations).
- The student demonstrates a conceptual understanding of geometric drawings or constructions.
Grade 9
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates an understanding of geometric relationships.
- The student solves problems (including real-world situations).
- The student demonstrates a conceptual understanding of geometric drawings or constructions.
Grade 10
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates an understanding of geometric relationships.
- The student solves problems (including real-world situations).
- The student demonstrates a conceptual understanding of geometric drawings or constructions.
Grade 5
-
Measurement and Geometry
- 1.0 Students understand and compute the volumes and areas of simple objects
Grade 7
-
Measurement and Geometry
- 2.0 Students compute the perimeter, area, and volume of common geometric objects and use the results to find measures of less common objects. They know how perimeter, area, and volume are affected by changes of scale
Third Grade
-
Measurement and Data
- Solve problems involving measurement and estimation of intervals of time, liquid volumes, and masses of objects.
- Geometric measurement: understand concepts of area and relate area to multiplication and to addition.
Fifth Grade
-
Measurement and Data
- Geometric measurement: understand concepts of volume and relate volume to multiplication and to addition.
Sixth Grade
-
Geometry
- Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving area, surface area, and volume.
Seventh Grade
-
Geometry
- Solve real-life and mathematical problems involving angle measure, area, surface area, and volume.
Geometry
-
Geometric Measurement and Dimension
- Explain volume formulas and use them to solve problems
- Visualize relationships between two-dimensional and three- dimensional objects
Grades 3-5
-
Measurement
- Apply appropriate techniques, tools, and formulas to determine measurements
Grades 6-8
-
Geometry
- Analyze characteristics and properties of two- and three-dimensional geometric shapes and develop mathematical arguments about geometric relationships
- Use visualization, spatial reasoning, and geometric modeling to solve problems
-
Measurement
- Apply appropriate techniques, tools, and formulas to determine measurements
Grades 9-12
-
Geometry
- Use visualization, spatial reasoning, and geometric modeling to solve problems
-
Measurement
- Apply appropriate techniques, tools, and formulas to determine measurements
Grade 7
-
Number and Operations, Measurement, Geometry, Data Analysis and Probability, Algebra
- COMPETENCY GOAL 2: The learner will understand and use measurement involving two- and three-dimensional figures.
- COMPETENCY GOAL 3: The learner will understand and use properties and relationships in geometry.
Grade 8
-
Number and Operations, Measurement, Geometry, Data Analysis and Probability, Algebra
- COMPETENCY GOAL 1: The learner will understand and compute with real numbers.
Introductory Mathematics
-
Geometry and Measurement
- COMPETENCY GOAL 2: The learner will use properties and relationships in geometry and measurement concepts to solve problems.
- COMPETENCY GOAL 2: The learner will understand and use measurement concepts.
-
Number and Operations
- COMPETENCY GOAL 1: The learner will understand and compute with real numbers.
Geometry
-
Geometry and Measurement
- Competency Goal 2: The learner will use geometric and algebraic properties of figures to solve problems and write proofs.
Technical Mathematics I
-
Geometry and Measurement
- Competency Goal 2: The learner will measure and apply geometric concepts to solve problems.
Technical Mathematics II
-
Geometry and Measurement
- Competency Goal 1: The learner will use properties of geometric figures to solve problems.
Integrated Mathematics III
-
Geometry and Measurement
- Competency Goal 2: The learner will use properties of geometric figures to solve problems.
Grade 5
-
Measurement
- 10. The student applies measurement concepts involving length (including perimeter), area, capacity/volume, and weight/mass to solve problems.
Grade 8
-
Measurement
- 8. The student uses procedures to determine measures of three-dimensional figures.
Textbooks Aligned
Grade Seven
-
Filling and Wrapping
- Investigation Two: Designing Packages
- Investigation Three: Finding Volumes of Boxes
- Investigation Six: Scaling Boxes
Book 1
-
Module 7 - Wonders of the World
- Section 2: Volumes of Prisms
Book 2
-
Module 6 - Flights of Fancy
- Section 2: Square Roots
- Section 2: Surface Area of Prisms
- Section 2: Area of a Circle
- Section 5: Volume of a Prism
- Section 5: Metric Units
- Section 5: Weighted Networks
Book 3
-
Module 1 - Amazing Feats, Facts and Fictions
- Section 4: Finding Circumferences
- Section 4: Finding Volumes
-
Module 3 - The Mystery of Blacktail Canyon
- Section 1: Square Roots
- Section 1: Length, Area
- Section 1: Volume
6th
-
Module 7 - Wonders of the World
-
Section 1: Three-Dimensional Geometry
- Reason for Alignment: Surface Area and Volume lesson guides the students through relationships in geometry. The textbook does not address surface area as such at this point, but volume and area are explored, so this shouldn't be a problem if the teacher wants to take the class a little further with the worksheet used in the lesson.
-
Section 1: Three-Dimensional Geometry
7th
-
Module 6 - Flights of Fancy
-
Section 3: Square Roots, Surface Area, and Area of a Circle
- Reason for Alignment: This lesson can be used for the section on surface area at this time, if that fits the needs of the teacher and the class. The discussion and the worksheets can easily be adapted.
-
Section 3: Square Roots, Surface Area, and Area of a Circle
-
Module 7 - MATH-Thematical Mix
-
Section 1: Measurement and Volume
- Reason for Alignment: This lesson was recommended in section 1 for its use of surface area. It can be used effectively here now as well, especially because students are now working with volume too.
-
Section 1: Measurement and Volume
8th
-
Module 3 - The Mystery of Blacktail Canyon
- Section 1: Square Roots and Measurement
-
Module 4 - Inventions
-
Section 1: Circumference, Area, and Volume
- Reason for Alignment: This lesson only uses for prisms so could be applied for that part of the section only. The accompanying worksheet contains questions for use with rectangular and triangular prisms.
-
Section 1: Circumference, Area, and Volume
-
Module 5 - Architects and Engineers
-
Section 4: Surface Area and Volume
- Reason for Alignment: Though this lesson has been recommended in other modules it would fit here as well. It accompanies the Surface Area and Volume activity.
-
Section 4: Surface Area and Volume
Book 3
-
Shapes and Space
- Lesson 3: Take One For Good Measure
- Lesson 5: All Boxed Up
Grade 5
-
Side Seeing
- Top and Side Views of three dimensional shapes
Grade 6
-
Made to Measure
- Volume
- Surface Area
-
Reallotment
- Estimating Area
- Surface Area
- Volume
Grade 7
-
Cereal Numbers
- Volume
- Surface Area
- Relationship between Volume and Surface Area
Be Prepared to
- answer the question "What is a prism?"
- discuss surface area and volume
- Define:
- base of the triangular prism
- height of the triangular prism
- width of the triangular prism
- base depth of the triangular prism