North Carolina Standard Course of Study
Discrete Mathematics
Algebra
Competency Goal 3: The learner will describe and use recursively-defined relationships to solve problems.
Lessons (2)
Introduces students to the ideas involved in understanding fractals.
Introduces students to arithmetic and geometric sequences. Students explore further through producing sequences by varying the starting number, multiplier, and add-on.
Activities (12)
Students work step-by-step through the generation of a different Hilbert-like Curve (a fractal made from deforming a line by bending it), allowing them to explore number patterns in sequences and geometric properties of fractals.
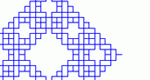
Generate complicated geometric fractals by specifying starting polygon and scale factor.
Step through the generation of a Hilbert Curve -- a fractal made from deforming a line by bending it, and explore number patterns in sequences and geometric properties of fractals.
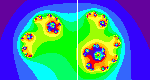
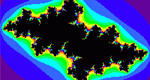
Enter a complex value for "c" in the form of an ordered pair of real numbers. The applet draws the fractal Julia set for that seed value.
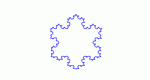
Step through the generation of the Koch Snowflake -- a fractal made from deforming the sides of a triangle, and explore number patterns in sequences and geometric properties of fractals.
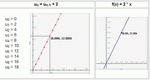
Graph recursive functions by defining f(0)=C and defining f(n) based on f(n-1).
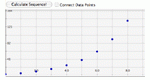
Learn about number patterns in sequences and recursions by specifying a starting number, multiplier, and add-on. The numbers in the sequence are displayed on a graph, and they are also listed below the graph.
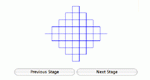
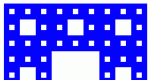
Step through the generation of Sierpinski's Carpet -- a fractal made from subdividing a square into nine smaller squares and cutting the middle one out. Explore number patterns in sequences and geometric properties of fractals.
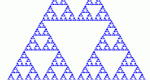
Step through the generation of Sierpinski's Triangle -- a fractal made from subdividing a triangle into four smaller triangles and cutting the middle one out. Explore number patterns in sequences and geometric properties of fractals.
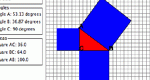
Learn about how the Pythagorean Theorem works through investigating the standard geometric proof. Parameters: Sizes of the legs of the triangle.
Explore fractals by investigating the relationships between the Mandelbrot set and Julia sets.
Enter two complex numbers (z and c) as ordered pairs of real numbers, then click a button to iterate step by step. The iterates are graphed in the x-y plane and printed out in table form. This is an introduction to the idea of prisoners/escapees in iterated functions and the calculation of fractal Julia sets.