North Carolina Standard Course of Study
AP Statistics
Data Analysis and Probability
Competency Goal 3: The learner will collect and analyze data to solve problems.
Activities (21)
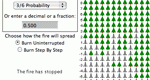
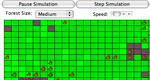
Students run a simulation of how a fire will spread through a stand of trees, learning about probability and chaos. Parameters: Forest density, wind direction, size of forest.
Run a simulation of how a fire spreads through a stand of trees, learning about probability and chaos. Track the results of multiple burns and use the data to draw conclusions.
Choose one of N doors to experimentally determine the odds of winning the grand prize behind one of the doors, as in the TV program "Let's Make a Deal." Parameters: Number of doors, number of trials, staying or switching between the two remaining doors.
Enter data to create a bar graph, then change many settings for the graph's appearance.
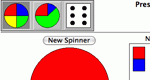
Create a game spinner with one to twelve sectors in order to look at experimental and theoretical probabilities. Parameters: Number of sectors, number of trials.
Enter your own data categories and the value of each category to create a pie chart. There are also built in data sets which can be viewed.
Simulation of a coin toss allowing the user to input the number of flips. Toss results can be viewed as a list of individual outcomes, ratios, or table.
Compare theoretical and experimental probabilities, using dice, cards, spinners, or coin tosses. Three different probabilities can be compared at once. Parameters: Type of probabilities, number of trials.
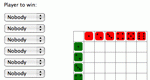
Experiment with the outcome distribution for a roll of two dice by simulating a dice throwing game. Parameters: Which player wins with which total rolled.
Run a simulation of how a fire will spread through a stand of trees, learning about probability and chaos. Parameters: Probability that a tree will set fire to each of its eight neighbors.
Experiment with probability using a fixed size section spinner, a variable section spinner, two regular 6-sided dice or customized dice.
Run a simulation of how a fire will spread through a stand of trees, learning about probability and chaos. Parameters: Probability that a tree catches fire if its neighbor is on fire.
Run a simulation to generate results from running the Monty Hall for multiple trials. This is similar to the game show "Let's Make A Deal", where you choose one of N doors in hopes of finding a grand prize behind one of the doors. Parameters: Number of doors, number of trials, staying, or switching between the two remaining doors.
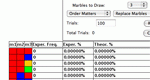
Learn about sampling with and without replacement by randomly drawing marbles from a bag. Parameters: Number and color of marbles in the bag, replacement rule.
Enter data to create a double bar graph, then manipulate the graph's maximum and minimum values.
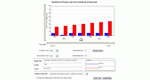
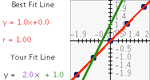
Students compare multiple independent variables as predictors of one dependent variable. Students explore correlation and lines of best-fit.
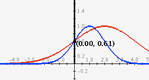
In this applet you can adjust the parameters on two Gaussian curves to determine if there is a possibility of a difference between the two means.
Create a pie chart, adjusting the size of the divisions using your mouse or by entering values. Parameters: Number of sections, size of sections, whether to use percents or fractions.
Experiment with a simple ecosystem consisting of grass, rabbits, and wolves, learning about probabilities, chaos, and simulation.
Choose one of three doors to experimentally determine the odds of winning the grand prize behind one of the doors, as in the TV program "Let's Make a Deal." Parameters: Staying or switching between the two remaining doors.
Models how a population of susceptible, infected, and recovered people is affected by a disease.