Common Core State Standards
Eighth Grade
Geometry
Understand congruence and similarity using physical models, trans- parencies, or geometry software.
Lessons (2)
Introduces students to the ideas involved in understanding fractals.
Introduces students to concepts of transformations.
Activities (7)
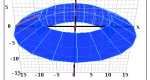
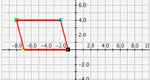
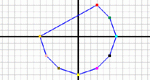
Build your own polygon and transform it in the Cartesian coordinate system. Experiment with reflections across any line, revolving around any line (which yields a 3-D image), rotations about any point, and translations in any direction.
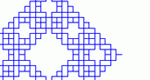
Students work step-by-step through the generation of a different Hilbert-like Curve (a fractal made from deforming a line by bending it), allowing them to explore number patterns in sequences and geometric properties of fractals.
Step through the generation of a Hilbert Curve -- a fractal made from deforming a line by bending it, and explore number patterns in sequences and geometric properties of fractals.
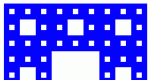
Step through the generation of Sierpinski's Carpet -- a fractal made from subdividing a square into nine smaller squares and cutting the middle one out. Explore number patterns in sequences and geometric properties of fractals.
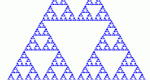
Step through the generation of Sierpinski's Triangle -- a fractal made from subdividing a triangle into four smaller triangles and cutting the middle one out. Explore number patterns in sequences and geometric properties of fractals.
Explore the world of translations, reflections, and rotations in the Cartesian coordinate system by transforming squares, triangles and parallelograms. Parameters: Shape, x or y translation, x or y reflection, angle of rotation.
Build your own polygon and transform it in the Cartesian coordinate system. Experiment with reflections across any line, rotations about any point, and translations in any direction. Parameters: Shape, x or y translation, x or y reflection, angle of rotation