South Carolina Academic Standards for Mathematics
Geometry
Geometry
Standard G-2: The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of the properties of basic geometric figures and the relationships between and among them.
Lessons (5)
Introduces students to acute, obtuse, and right angles as well as relationships between angles formed by parallel lines crossed by a transversal.
Introduces students to arithmetic and geometric sequences. Students explore further through producing sequences by varying the starting number, multiplier, and add-on.
Introduces students to length, perimeter and area.
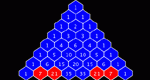
Looks at how Pascal's Triangle can be used to generate Sierpinski triangle-like results.
Students learn to identify a variety of patterns using sequences and tessellations.
Activities (4)
Color numbers in Pascal's Triangle by rolling a number and then clicking on all entries that have the same remainder when divided by the number rolled, thereby practicing division and remainders, investigating number patterns, and investigating fractal patterns. Coloring Remainders in Pascal's Triangle is one of the Interactivate assessment explorers.
Recognize patterns in a series of shapes, numbers, or letters. After determining the pattern, the student fills in the missing pieces. Three levels of difficulty are available.
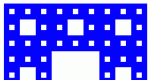
Step through the generation of Sierpinski's Carpet -- a fractal made from subdividing a square into nine smaller squares and cutting the middle one out. Explore number patterns in sequences and geometric properties of fractals.
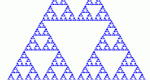
Step through the generation of Sierpinski's Triangle -- a fractal made from subdividing a triangle into four smaller triangles and cutting the middle one out. Explore number patterns in sequences and geometric properties of fractals.