NCTM
Grades 9-12
Algebra
Analyze change in various contexts
Lessons (1)
Explores derivatives and the idea of infinity using a geometric interpretation of slope.
Activities (12)
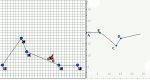
Enter a set of data points, then derive a function to fit those points. Manipulate the function on a coordinate plane using slider bars. Learn how each constant and coefficient affects the resulting graph.
View the graph and the equation of the line tangent to any function at any point on the function.
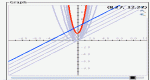
A more advanced version of Slope Slider, this activity allows the manipulation of the constants and coefficients in any function thereby encouraging the user to explore the effects on the graph of the function by changing those numbers.
Students can create graphs of functions entered as algebraic expressions -- similar to a graphing calculator.
Create graphs of functions and sets of ordered pairs on the same coordinate plane. This is like a graphing calculator with advanced viewing options.
This applet allows the user to make observations about the relationship between speed and position and how both of these are affected by initial velocity and the incline on which the biker is traveling.
Enter a set of data points and a function or multiple functions, then manipulate those functions to fit those points. Manipulate the function on a coordinate plane using slider bars. Learn how each constant and coefficient affects the resulting graph.
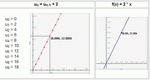
Graph recursive functions by defining f(0)=C and defining f(n) based on f(n-1).
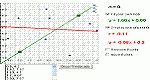
Plot a bivariate data set, determine the line of best fit for their data, and then check the accuracy of your line of best fit.
Graph ordered pairs and customize the graph title and axis labels. Points are connected from left to right, rather than being connected in the order they are entered.
Plot ordered pairs of numbers, either as a scatter plot or with the dots connected. Points are connected from right to left, rather than being connected in the order they are entered.
Similar to other "flyers", Slope Slider uses slider bars to explore the effect of the multiplier and constant on a linear function of the form f(x)=mx+b. Explore the relationship between slope and intercept in the Cartesian coordinate system.