NCTM
Grades 9-12
Data Analysis and Probability
Formulate questions that can be addressed with data and collect, organize, and display relevant data to answer them
Lessons (4)
Introduction and fine points of using bar graphs and histograms.
Introduces statistical measures of center.
Students are introduced to correlation between two variables and the line of best fit.
Introduces the normal distribution and looks at the bell curve controversy.
Activities (28)
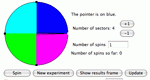
Create a game spinner with variable sized sectors to look at experimental and theoretical probabilities. Parameters: Sizes of sectors, number of sectors, number of trials.
Run a simulation of how a fire spreads through a stand of trees, learning about probability and chaos. Track the results of multiple burns and use the data to draw conclusions.
Choose one of N doors to experimentally determine the odds of winning the grand prize behind one of the doors, as in the TV program "Let's Make a Deal." Parameters: Number of doors, number of trials, staying or switching between the two remaining doors.
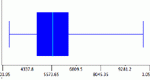
Students can create box plots for either built-in or user-specified data as well as experiment with outliers. User may choose to use or not use the median for calculation of interquartile range.
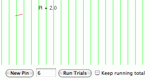
Experiment with a simulation to get an approximation of Pi by dropping a needle on a lined sheet of paper.
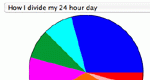
Enter your own data categories and the value of each category to create a pie chart. There are also built in data sets which can be viewed.
Simulation of a coin toss allowing the user to input the number of flips. Toss results can be viewed as a list of individual outcomes, ratios, or table.
Compare theoretical and experimental probabilities, using dice, cards, spinners, or coin tosses. Three different probabilities can be compared at once. Parameters: Type of probabilities, number of trials.
Experiment with the outcome distribution for a roll of two dice by simulating a dice throwing game. Parameters: Which player wins with which total rolled.
Experiment with probability using a fixed size section spinner, a variable section spinner, two regular 6-sided dice or customized dice.
This applet allows the user to experiment with randomly generated data sets at various sample sizes and standard deviations. Then, users can compare the distribution of the experimental data to the expected distribution.
Run a simulation to generate results from running the Monty Hall for multiple trials. This is similar to the game show "Let's Make A Deal", where you choose one of N doors in hopes of finding a grand prize behind one of the doors. Parameters: Number of doors, number of trials, staying, or switching between the two remaining doors.
View histograms for built-in or user-specified data. Experiment with how the size of the class intervals influences the appearance of the histogram. Parameters: Data sets, class sizes.
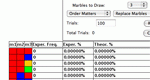
Learn about sampling with and without replacement by randomly drawing marbles from a bag. Parameters: Number and color of marbles in the bag, replacement rule.
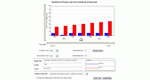
Enter data and view the mean, median, variance, and standard deviation of the data set. Parameters: Number of observations, range for observations, which statistics to view, identifiers for the data.
Enter data to create a double bar graph, then manipulate the graph's maximum and minimum values.
Students compare multiple independent variables as predictors of one dependent variable. Students explore correlation and lines of best-fit.
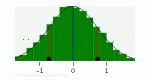
Change the standard deviation of an automatically generated normal distribution to create a new histogram. Observe how well the histogram fits the curve, and how areas under the curve correspond to the number of trials. Parameters: standard deviation, number of trials, class intervals.
In this applet you can adjust the parameters on two Gaussian curves to determine if there is a possibility of a difference between the two means.
Create a pie chart, adjusting the size of the divisions using your mouse or by entering values. Parameters: Number of sections, size of sections, whether to use percents or fractions.
PlopIt allows users to build dot plots of data using the mouse. View how the mean, median, and mode change as entries are added to the plot. Parameters: Range for observations.
Simulate a game where two players each roll a die, and the lucky player moves one step to the finish. Parameters: what rolls win and how many steps to the finish line.
Simulate a game where "N" players roll two dice, and the lucky player has an advantage for reaching the finish. Parameters: the number of players, number of trials and length of the race.
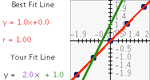
Plot a bivariate data set, determine the line of best fit for their data, and then check the accuracy of your line of best fit.
Graph ordered pairs and customize the graph title and axis labels. Points are connected from left to right, rather than being connected in the order they are entered.
Choose one of three doors to experimentally determine the odds of winning the grand prize behind one of the doors, as in the TV program "Let's Make a Deal." Parameters: Staying or switching between the two remaining doors.
Change the median and standard deviation of an automatically generated normal distribution to create a skewed distribution, allowing you to observe properties like what it means for the mean, median, and mode to be different. Parameters: median, standard deviation, number of trials, class intervals.
View stem-and-leaf plots of your own data, and then practice finding means, medians and modes. Stem and Leaf Plotter is one of the Interactivate assessment explorers.