NCTM
Grades 9-12
Geometry
Analyze characteristics and properties of two- and three-dimensional geometric shapes and develop mathematical arguments about geometric relationships
Lessons (15)
Introduces students to acute, obtuse, and right angles as well as relationships between angles formed by parallel lines crossed by a transversal.
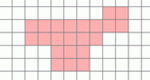
Comparing shapes with the same areas but different perimeters.
This lesson utilizes the concepts of cross-sections of three-dimensional figures to demonstrate the derivation of two-dimensional shapes.
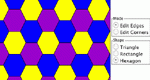
Explores lines, planes, angles, and polygons in tessellations.
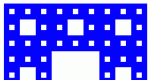
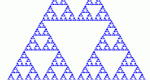
Introduces students to the ideas involved in understanding fractals.
Introduces students to quadrilaterals with an emphasis on defining characteristics of parallelograms, rectangles, and trapezoids.
Introduces students to lines, rays, line segments, and planes.
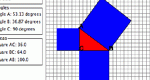
Students learn how the Pythagorean Theorem works and how to apply it.
Introduces students to the concepts of surface area and volume.
This lesson teaches students how to find the surface area of non-rectangular prisms.
This lesson teaches students how to find the surface area of rectangular prisms.
Examines plane symmetry.
Explore the mathematical nature of art and tilings and looks at the role of math in nature and our culture.
This lesson teaches students how to find the volume of non-rectangular prisms.
This lesson teaches students how to find the volume of rectangular prisms.
Activities (11)
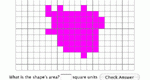
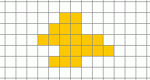
Learn the relationship between perimeter and area. A shape will be automatically generated with the perimeter that you choose. Calculate the area of this shape. Area Explorer is one of the Interactivate assessment explorers.
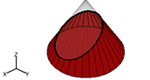
Explore cross sections of different geometric solids: cone, double cone, cylinder, pyramid, and prism. Manipulate the cross section with slider bars, and see how the graphical representation changes.
Build a "floor tile" by dragging the corners of a quadrilateral. Learn about tessellation of quadrilateral figures when the shape you built is tiled over an area.
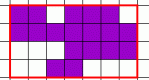
Learn the relationship between perimeter and area. A shape will be automatically generated with the area that you choose. Calculate the perimeter of this shape. Perimeter Explorer is one of the Interactivate assessment explorers.
This activity operates in one of two modes: auto draw and create shape mode, allowing you to explore relationships between area and perimeter. Shape Builder is one of the Interactivate assessment explorers.
Learn the relationship between perimeter and area. A random shape will be automatically generated. Calculate the area and perimeter of this shape. Shape Explorer is one of the Interactivate assessment explorers.
Step through the generation of Sierpinski's Carpet -- a fractal made from subdividing a square into nine smaller squares and cutting the middle one out. Explore number patterns in sequences and geometric properties of fractals.
Step through the generation of Sierpinski's Triangle -- a fractal made from subdividing a triangle into four smaller triangles and cutting the middle one out. Explore number patterns in sequences and geometric properties of fractals.
Learn about how the Pythagorean Theorem works through investigating the standard geometric proof. Parameters: Sizes of the legs of the triangle.
Create a tessellation by deforming a triangle, rectangle or hexagon to form a polygon that tiles the plane. Corners of the polygons may be dragged, and corresponding edges of the polygons may be dragged. Parameters: Colors, starting polygon.
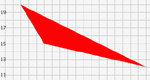
Calculate the area of a triangle drawn on a grid. Learn about areas of triangles and about the Cartesian coordinate system. Triangle Explorer is one of the Interactivate assessment explorers.