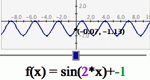Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills
Algebra I
Quadratic and Other Nonlinear Functions
11. The student understands there are situations modeled by functions that are neither linear nor quadratic and models the situations.
Activities (8)
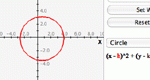
Manipulate different types of conic section equations on a coordinate plane using slider bars. Learn how each constant and coefficient affects the resulting graph. Choose from vertical or horizontal parabola, circle, ellipse, and vertical or horizontal hyperbola.
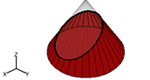
Explore cross sections of different geometric solids: cone, double cone, cylinder, pyramid, and prism. Manipulate the cross section with slider bars, and see how the graphical representation changes.
Enter a set of data points, then derive a function to fit those points. Manipulate the function on a coordinate plane using slider bars. Learn how each constant and coefficient affects the resulting graph.
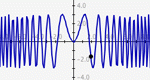
A more advanced version of Slope Slider, this activity allows the manipulation of the constants and coefficients in any function thereby encouraging the user to explore the effects on the graph of the function by changing those numbers.
Students can create graphs of functions entered as algebraic expressions -- similar to a graphing calculator.
Create graphs of functions and sets of ordered pairs on the same coordinate plane. This is like a graphing calculator with advanced viewing options.
Enter a set of data points and a function or multiple functions, then manipulate those functions to fit those points. Manipulate the function on a coordinate plane using slider bars. Learn how each constant and coefficient affects the resulting graph.
Students create linear inequalities and systems of linear inequalities on a coordinate plane. This is like a graphing calculator with advanced viewing options.