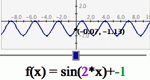Mathematics in Context Grade 7
Packages and Polygons
Models
Activities (12)
Enter a set of data points, then derive a function to fit those points. Manipulate the function on a coordinate plane using slider bars. Learn how each constant and coefficient affects the resulting graph.
A more advanced version of Slope Slider, this activity allows the manipulation of the constants and coefficients in any function thereby encouraging the user to explore the effects on the graph of the function by changing those numbers.
Students can create graphs of functions entered as algebraic expressions -- similar to a graphing calculator.
Create graphs of functions and sets of ordered pairs on the same coordinate plane. This is like a graphing calculator with advanced viewing options.
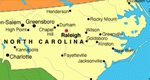
Measure angles, distances, and areas in several different images (choices include maps, aerial photos, and others). A scale feature allows the user to set the scale used for measuring distances and areas.
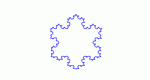
Step through the generation of the Koch Snowflake -- a fractal made from deforming the sides of a triangle, and explore number patterns in sequences and geometric properties of fractals.
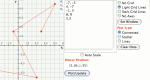
Plot ordered pairs on the graph, and they will be connected in the order that they are input. This enables you to decide how the pairs should be connected, rather than having the computer connect them from left to right.
Review the properties of functions by looking at ten different curves and deciding whether or not they meet the criteria for a graph of a function. This activity simply displays the curves - it does not quiz the user.
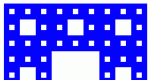
Step through the generation of Sierpinski's Carpet -- a fractal made from subdividing a square into nine smaller squares and cutting the middle one out. Explore number patterns in sequences and geometric properties of fractals.
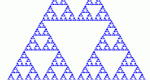
Step through the generation of Sierpinski's Triangle -- a fractal made from subdividing a triangle into four smaller triangles and cutting the middle one out. Explore number patterns in sequences and geometric properties of fractals.
Plot ordered pairs of numbers, either as a scatter plot or with the dots connected. Points are connected from right to left, rather than being connected in the order they are entered.
Enter two complex numbers (z and c) as ordered pairs of real numbers, then click a button to iterate step by step. The iterates are graphed in the x-y plane and printed out in table form. This is an introduction to the idea of prisoners/escapees in iterated functions and the calculation of fractal Julia sets.