What is Angles?
This activity allows the user to practice important angle vocabulary. Line l is parallel to line m. Also line r is parallel to line s. Each of the angles formed by the intersection of these four parallel lines can be classified as acute, obtuse, or right.
- acute angle - an angle whose measure is less than 90 degrees
- obtuse angle - an angle whose measure is greater than 90 degrees
- right angle - an angle whose measure is 90 degrees
Any pair of angles can be classified as adjacent, vertical, alternate-interior, alternate-exterior, same-side interior, same-side exterior, corresponding, or as none of the above.
- adjacent angles - two angles that share a ray, thereby being directly next to each other
- alternate exterior angles - angles located outside a set of parallel lines and on opposite sides of the transversal.
- alternate interior angles - angles located inside a set of parallel lines and on opposite sides of the transversal.
- vertical angles - angles that share only one point. They are on opposite sides of the transversal.
- corresponding angles - angles that are at corresponding positions to each other. They are on the same side of the transversal.
- same-side interior angles - angles located inside a set of parallel lines and on the same side of the transversal.
- same-side exterior angles - angles located outside a set of parallel lines and on the same side of the transversal.
How Do I Use This Activity?
This activity allows the user to practice important angle vocabulary.
Controls and Output
-
The program provides an illustration of two parallel lines. You can choose whether the lines
are cut by one or two transversals.
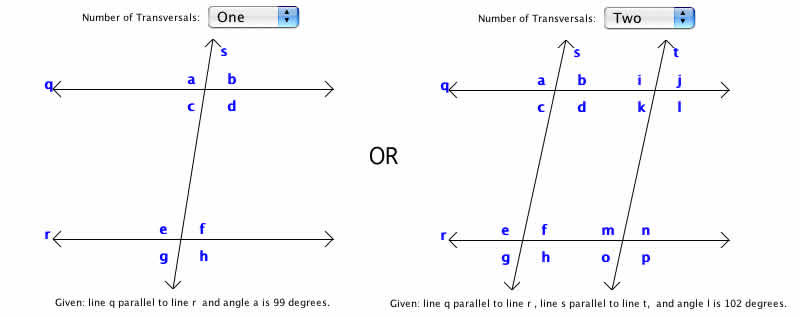
- Examine the given information that appears below the drawing. It displays the measure of one of the angles in the diagram and gives which lines are parallel to each other.
-
The program will ask you to identify two angles as either obtuse, acute, or right. Use the
pull-down choices to answer:
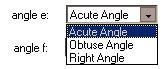
-
The program then asks that you specify a relationship between the two angles. Once again,
use the pull-down choices to choose either vertical, adjacent, alternate-interior,
alternate-exterior, same-side interior, same-side exterior, corresponding, or none of the
above:

-
After you believe you have correctly identified the three answers, click the
Check Answer button to see if you are correct:
-
In order to get a new question, click the
New Angles button:

Scoring
- This activity will automatically record how successful you are at answering the questions. To view the score, press the Show Score button at the bottom of the activity and a pop-up window will appear with the scoreboard. To close this pop-up window press the Close button or click back on the main window.
- To pause the scoring, press the Active button at the bottom of the screen and it will change to a Paused button. To resume scoring, press the Paused button.
- To reset the scoreboard, open the scoreboard using the Show Score button and then press the Reset button.
Because this activity randomly generates questions, a feature called Seed Random has been implemented that allows multiple users using different computers to work on the same problem. See Seed Random Help for instructions on using this feature.
Description
This activity allows the user to practice important angle vocabulary. This activity would work well in mixed ability groups of two or three for about twenty to twenty-five minutes if you use the exploration questions and ten to fifteen minutes otherwise.
Place in Mathematics Curriculum
This activity can be used to:
- Identify pairs of angles with special relationships: supplementary, complementary, vertical, adjacent, etc.
- Discuss parallel lines.
Standards Addressed
Grade 6
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates an understanding of geometric relationships.
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of similarity, congruence, symmetry, or transformations of shapes.
- The student solves problems (including real-world situations) using perimeter, area, or volume.
- The student demonstrates a conceptual understanding of geometric drawings or constructions.
Grade 7
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates an understanding of geometric relationships.
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of similarity, congruence, symmetry, or transformations of shapes.
- The student solves problems (including real-world situations).
- The student demonstrates a conceptual understanding of geometric drawings or constructions.
Grade 8
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates an understanding of geometric relationships.
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of similarity, congruence, symmetry, or transformations of shapes.
- The student solves problems (including real-world situations).
- The student demonstrates a conceptual understanding of geometric drawings or constructions.
Grade 9
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates an understanding of geometric relationships.
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of similarity, congruence, symmetry, or transformations of shapes.
- The student solves problems (including real-world situations).
- The student demonstrates a conceptual understanding of geometric drawings or constructions.
Grade 10
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates an understanding of geometric relationships.
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of similarity, congruence, symmetry, or transformations of shapes.
- The student solves problems (including real-world situations).
- The student demonstrates a conceptual understanding of geometric drawings or constructions.
Fourth Grade
-
Geometry
- Draw and identify lines and angles, and classify shapes by properties of their lines and angles.
-
Measurement and Data
- Geometric measurement: understand concepts of angle and measure angles.
Seventh Grade
-
Geometry
- Solve real-life and mathematical problems involving angle measure, area, surface area, and volume.
Geometry
-
Congruence
- Prove geometric theorems
Grades 9-12
-
Geometry
- Use visualization, spatial reasoning, and geometric modeling to solve problems
Grade 6
-
Number and Operations, Measurement, Geometry, Data Analysis and Probability, Algebra
- COMPETENCY GOAL 2: The learner will select and use appropriate tools to measure two- and three-dimensional figures.
Grade 8
-
Number and Operations, Measurement, Geometry, Data Analysis and Probability, Algebra
- COMPETENCY GOAL 3: The learner will understand and use properties and relationships in geometry.
Introductory Mathematics
-
Data Analysis and Probability
- COMPETENCY GOAL 3: The learner will understand and use properties and relationships in geometry.
-
Geometry and Measurement
- COMPETENCY GOAL 2: The learner will use properties and relationships in geometry and measurement concepts to solve problems.
Geometry
-
Geometry and Measurement
- Competency Goal 2: The learner will use geometric and algebraic properties of figures to solve problems and write proofs.
Technical Mathematics I
-
Geometry and Measurement
- Competency Goal 2: The learner will measure and apply geometric concepts to solve problems.
Technical Mathematics II
-
Geometry and Measurement
- Competency Goal 1: The learner will use properties of geometric figures to solve problems.
Integrated Mathematics III
-
Geometry and Measurement
- Competency Goal 2: The learner will use properties of geometric figures to solve problems.
5th Grade
-
Geometry
- 5.14 The student will classify angles and triangles as right, acute, or obtuse.
Be Prepared to
- Define and give examples of alternate interior, alternate exterior, adjacent, and corresponding angles
- Discuss parallel and perpendicular lines
- Define and show examples of right angles, obtuse angles, and acute angles
- Stop the students from classifying their peers as acute and obtuse people (it will happen)