What is Image Tool?
This activity allows the user to measure angles and explore the concept of "scale" as it pertains to maps, images, and drawings. The scale feature allows the user to define a scale and then using that scale, measure distances or areas on a selected image.
Understanding scale measurements requires understanding the concept of proportion. When using a scale model or drawing, a ratio is given such that a measurement taken from the model or drawing represents another measurement, presumably the "life size" measurement the model or drawing represents. This ratio can then be set equal to a second ratio where a second measurement is taken from the model or drawing in order to determine the unknown "life size" measurement.
For instance, say you have a map where 1 inch represents 100 miles. If you measure 3.5 inches on the map then that will represent 3.5 * 100 = 350 miles.
In order to determine scale area rather than scale distance, it is required to square the measurements because area is measured in square units. So if 1 inch represents 100 miles then 1 square inch represents 10,000 square miles. This also implies that 3.5 square inches represents 3.5 * 10,000 = 35,000 square miles.
How Do I Use This Activity?
This activity allows the user to measure angles and explore the concept of "scale" as it pertains to maps, images, and drawings. The scale feature allows the user to define a scale and then using that scale, measure distances or areas on a selected image. The activity also allows the user to measure angles on the image.
Controls and Output
-
First select the image you want to use from the drop down menu:
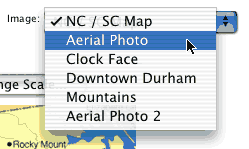
Note that if you would like to use your own non-copyrighted image, use the Activity Feedback located at the bottom of the page to contact us and we will coordinate uploading the image to the activity.
-
Next, select "distance" from the "measurement" menu in order to set your desired scale.

-
To set the scale, create a line with two endpoints on the image by clicking on the two endpoints, then click the "change scale" button.


-
A window will pop up after clicking on the "change scale" button asking you to define the
selected distance. Input the quantity and unit that the selected distance represents.
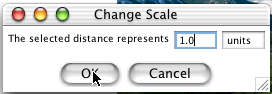
- You can now select other distances on the image by creating more line segments on the image. Use the Reset button to clear any distances already selected. Otherwise, a new line segment will be built using the last endpoint placed.
-
To measure
Area select "Area" from the "measurement menu." Then create a polygon on the image by clicking
on the verticies of where you want the polygon to lie in a clockwise or counterclockwise
fashion. Be sure to complete the polygon by clicking on the first endpoint as the ending
endpoint as well.
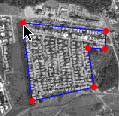
- The calculated distance or area is displayed based upon the scale you set under the "change scale" button.
- To measure an angle select "Angle" from the "measurement menu" and then create an angle by clicking on 3 points in the image to create an angle. The angle measure will be displayed.
Description
This activity allows the user to measure angles, distances, and areas in images. A scale feature allows the user to set the scale Image Tool uses for measuring distances and areas. This activity would work well in small groups of 2-3 for about 20-25 minutes if you use the exploration questions and 10-15 minutes otherwise.
Place in Mathematics Curriculum
This activity can be used to:
- Teach students about measurement of angles
- Show how area is measured
- Teach how travel distance is not the same as straight line distance
- Demonstrate ratio and proportion
- Teach students about scale measurements
Standards Addressed
Grade 6
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates an understanding of geometric relationships.
- The student demonstrates a conceptual understanding of geometric drawings or constructions.
Grade 7
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates an understanding of geometric relationships.
- The student demonstrates a conceptual understanding of geometric drawings or constructions.
Grade 8
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates an understanding of geometric relationships.
- The student demonstrates a conceptual understanding of geometric drawings or constructions.
Grade 9
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates an understanding of geometric relationships.
- The student demonstrates a conceptual understanding of geometric drawings or constructions.
Grade 10
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates an understanding of geometric relationships.
- The student demonstrates a conceptual understanding of geometric drawings or constructions.
Fourth Grade
-
Geometry
- Draw and identify lines and angles, and classify shapes by properties of their lines and angles.
Seventh Grade
-
Geometry
- Solve real-life and mathematical problems involving angle measure, area, surface area, and volume.
Number and Quantity
-
Quantities
- Reason quantitatively and use units to solve problems.
Geometry
-
Modeling with Geometry
- Apply geometric concepts in modeling situations
6th Grade
-
Measurement
- The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of surface area; the perimeter and area of irregular shapes; the relationships among the circumference, diameter, and radius of a circle; the use of proportions to determine
- The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of surface area; the perimeter and area of irregular shapes; the relationships among the circumference, diameter, and radius of a circle; the use of proportions to determine unit rates; and the use of scale to determine distance.
Geometry
-
Geometry
- Standard G-1: The student will understand and utilize the mathematical processes of problem solving, reasoning and proof, communication, connections, and representation.
7th Grade
-
Computation and Estimation
- 7.6 The student will use proportions to solve practical problems, which may include scale drawings, that contain rational numbers (whole numbers, fractions, and decimals) and percents.
-
Measurement
- 7.7 The student, given appropriate dimensions, will
- 7.7a The student, given appropriate dimensions, will estimate and find the area of polygons by subdividing them into rectangles and right triangles
8th Grade
-
Computation and Estimation
- 8.3 The student will solve practical problems involving rational numbers, percents, ratios, and proportions. Problems will be of varying complexities and will involve real-life data, such as finding a discount and discount prices and balancing a checkbook.
- 8.3 The student will solve practical problems involving rational numbers, percents, ratios, and proportions. Problems will be of varying complexities and will involve real-life data,
-
Measurement
- 8.6 The student will verify by measuring and describe the relationships among vertical angles, supplementary angles, and complementary angles and will measure and draw angles of less than 360°.
- 8.6 The student will verify by measuring and describe the relationships among vertical
Textbooks Aligned
Grade Six
-
Covering and Surrounding
- Investigation One: Measuring Perimeter and Area
- Investigation Three: Constant Area, Changing Perimeter
- Investigation Five: Measuring Parallelograms
-
Shapes and Designs
- Investigation Three: Polygons and Angles
Grade Eight
-
Looking for Pythagoras
- Investigation Two: Finding Areas and Lengths
Book 1
-
Module 6 - Comparisons and Predictions
- Section 5: Models and Scale Drawings
- Section 5: Measuring Angles
-
Module 7 - Wonders of the World
- Section 1: Customary Units for Area
Book 2
-
Module 2 - Search and Rescue
- Section 1: Measuring Angles
- Section 1: Angle Relationships
-
Module 6 - Flights of Fancy
- Section 1: Areas of Polygons
- Section 3: Scale Drawing and Similarity
Book 3
-
Module 1 - Amazing Feats, Facts and Fictions
- Section 6: Area, Perimeter
6th
-
Module 6 - Comparisons and Predictions
- Section 5: Geometry and Proportions
7th
-
Module 4 - The Art of Motion
- Section 6: Translations, Similarity, and Two-Step Equations
8th
-
Module 5 - Architects and Engineers
- Section 6: Scale Drawings and Similar Figures
Book 1
-
Designing Spaces
- Lesson 6: Polygon Paths
- Lesson 8: Assembling the Pieces
Book 2
-
From the Ground Up
- Lesson 7: Determining Roof Area
- Lesson 8: Calculating Roof Cost
- Lesson 9: Costs of Floors and Ceilings
-
Getting In Shape
- Lesson 1: The Angle on Angles
Book 3
-
Roads and Ramps
- Lesson 1: Slopes and Slope-o-meters
- Lesson 4: Right Triangles
Grade 5
-
Figuring All the Angles
- Measuring Angles
- Vectors
- Rectangular Coordinates
- Polar Coordinates
-
Grasping Sizes
- Ratios
- Proportional Enlargements and Reductions
- Scale Lines
- Calculating Ratios
Grade 6
-
Made to Measure
- Length
- Volume
- Surface Area
- English Units
- Metric Units
-
Ratios and Rates
- Ratio/Fraction/Decimal/Percent Relationships
- Part-Part Ratios
- Part-Whole Ratios
- Scale Factor
- Linear Functions
-
Reallotment
- Estimating Area
- Perimeter
- Surface Area
- Volume
- English and Metric Units
Grade 7
-
Cereal Numbers
- Volume
- Surface Area
- Relationship between Volume and Surface Area
- Comparisons with Ratios
- Fractions
- Decimals and Percents
- Multiplying and Dividing Fractions
-
Looking at an Angle
- Vision Lines
- Isomorphisms
- Tangent Ratios
-
Packages and Polygons
- Geometric Shapes
- Models
- Properties of Regular and Semi-Regular Polyhedra
Be Prepared to
- Explain the concept of ratio and proportion
- Explain how changing the scale effect the length and area mesurements
- Discuss how the scale relates to actual distance on each map
- Show students how to move points and how to start over