What is Perimeter Explorer?
This activity allows the user to test his or her skill at calculating the perimeter of a random shape. The user is given a random shape and allowed to enter a value for the perimeter. The applet then informs the user whether or not the value is correct. The user may continue trying until he or she gets the correct answer.
Perimeter, the distance around a shape, is usually expressed with units. Perimeter is given in terms of the units used to measure distance, 3 feet or 6 meters, for example.
There are two systems of units that are commonly used: standard and metric. Most of America uses the standard system while many other countries use the metric system. Converting standard units to metric units is done by multiplying by a proportionality constant.
Here are the tables of proportionality constants for the units of length.
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
So, converting 8500 feet into kilometers would look like this:

How Do I Use This Activity?
This activity allows users to test their skills at calculating the perimeter of a random shape.
Controls and Output
-
The applet displays a random shape for you to calculate the perimeter. Enter the perimeter
of the current shape into the
What is the shape's perimeter? text field and click the
check answer button.

- A message will appear beside the text field letting the user know whether or not the answer is correct.
-
To get a new shape, click the
Draw New Shape button.

-
To draw only rectangles, be sure the
Only Draw Rectangular Shapes box is checked.
-
To change the area of the figure use the
Adjust Area scroll bar, and click the
Draw New Shape button.

-
Or you may enter a new area in
The shape's area is: text field and hit enter to adjust the area of the figure.
-
The
Compare Area and Perimeters button allows you to keep track of your previous correct answers in order to compare the
corresponding areas to a given perimeter or vice versa. Clicking this button brings up a
new window:
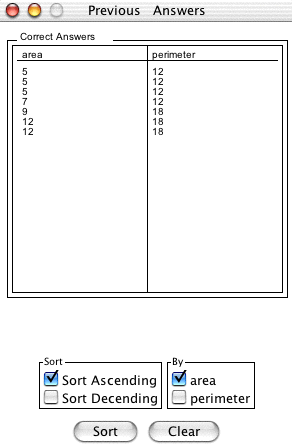
You can sort by either the area or perimeter from least to greatest. To sort by area, make sure the area check box is selected and to sort by perimeter, make sure the perimeter check box is selected and the click the sort button.
In order to return to the activity, simply click back in the main window (though if you are using Internet Explorer on OSX for Mac you will need to click on the title bar of the main window to return to the activity). To clear the data and keep the window open, click the clear button.
-
The
 button draws a red rectangular box around the figure on the grid. This can serve as a
hint in determining the figure's perimeter. Note that once the button is clicked it
toggles to read
button draws a red rectangular box around the figure on the grid. This can serve as a
hint in determining the figure's perimeter. Note that once the button is clicked it
toggles to read
 .
.
Scoring
- This activity will automatically record how successful you are at answering the questions. To view the score, press the Show Score button at the bottom of the activity and a pop-up window will appear with the scoreboard. To close this pop-up window press the Close button or click back on the main window.
- To pause the scoring, press the Active button at the bottom of the screen and it will change to a Paused button. To resume scoring, press the Paused button.
- To reset the scoreboard, open the scoreboard using the Show Score button and then press the Reset button.
Because this activity randomly generates questions, a feature called Seed Random has been implemented that allows multiple users using different computers to work on the same problem. See Seed Random Help for instructions on using this feature.
Description
This applet allows users to practice calculating the perimeter of random shapes. This activity would work well in mixed ability groups of two or three for about twenty-five minutes if you use the exploration questions and ten to fifteen minutes otherwise.
Place in Mathematics Curriculum
This activity can be used to:
- illustrate the notion of perimeter
- develop students' visualization skills
- practice students' skills at calculating perimeter
Standards Addressed
Grade 3
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates an understanding of geometric relationships.
- The student solves problems using perimeter or area.
- The student demonstrates a conceptual understanding of geometric drawings or constructions.
Grade 4
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates an understanding of geometric relationships.
- The student solves problems using perimeter or area.
- The student demonstrates a conceptual understanding of geometric drawings or constructions.
Grade 5
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates an understanding of geometric relationships.
- The student solves problems (including real-world situations) using perimeter or area.
- The student demonstrates a conceptual understanding of geometric drawings or constructions.
Grade 6
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates an understanding of geometric relationships.
- The student solves problems (including real-world situations) using perimeter, area, or volume.
- The student demonstrates a conceptual understanding of geometric drawings or constructions.
Grade 7
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates an understanding of geometric relationships.
- The student solves problems (including real-world situations).
- The student demonstrates a conceptual understanding of geometric drawings or constructions.
Grade 8
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates an understanding of geometric relationships.
- The student solves problems (including real-world situations).
- The student demonstrates a conceptual understanding of geometric drawings or constructions.
Grade 9
-
Geometry
- The student solves problems (including real-world situations).
Grade 10
-
Geometry
- The student solves problems (including real-world situations).
Grade 4
-
Measurement and Geometry
- 1.0 Students understand perimeter and area
Grade 7
-
Measurement and Geometry
- 2.0 Students compute the perimeter, area, and volume of common geometric objects and use the results to find measures of less common objects. They know how perimeter, area, and volume are affected by changes of scale
Third Grade
-
Geometry
- Reason with shapes and their attributes.
-
Measurement and Data
- Geometric measurement: recognize perimeter as an attribute of plane figures and distinguish between linear and area measures.
Number and Quantity
-
Quantities
- Reason quantitatively and use units to solve problems.
Grades 3-5
-
Measurement
- Apply appropriate techniques, tools, and formulas to determine measurements
Grades 6-8
-
Measurement
- Apply appropriate techniques, tools, and formulas to determine measurements
Grades 9-12
-
Geometry
- Analyze characteristics and properties of two- and three-dimensional geometric shapes and develop mathematical arguments about geometric relationships
-
Measurement
- Apply appropriate techniques, tools, and formulas to determine measurements
Grade 4
-
Number and Operations, Measurement, Geometry, Data Analysis and Probability, Algebra
- COMPETENCY GOAL 2: The learner will understand and use perimeter and area.
Grade 6
-
Number and Operations, Measurement, Geometry, Data Analysis and Probability, Algebra
- COMPETENCY GOAL 2: The learner will select and use appropriate tools to measure two- and three-dimensional figures.
Geometry
-
Geometry and Measurement
- Competency Goal 2: The learner will use geometric and algebraic properties of figures to solve problems and write proofs.
Technical Mathematics I
-
Geometry and Measurement
- Competency Goal 2: The learner will measure and apply geometric concepts to solve problems.
Technical Mathematics II
-
Geometry and Measurement
- Competency Goal 1: The learner will use properties of geometric figures to solve problems.
Integrated Mathematics
-
Geometry and Measurement
- Competency Goal 2: The learner will use properties of geometric figures to solve problems.
Integrated Mathematics III
-
Geometry and Measurement
- Competency Goal 2: The learner will use properties of geometric figures to solve problems.
6th Grade
-
Measurement
- The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of surface area; the perimeter and area of irregular shapes; the relationships among the circumference, diameter, and radius of a circle; the use of proportions to determine unit rates; and the use of scale to determine distance.
5th Grade
-
Measurement
- The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of the units and systems of measurement and the application of tools and formulas to determine measurements.
8th Grade
-
Measurement
- The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of the proportionality of similar figures; the necessary levels of accuracy and precision in measurement; the use of formulas to determine circumference, perimeter, area, and volume; and the use of conversions within and between the U.S. Customary System and the metric system.
Geometry
-
Geometry
- Standard G-4: The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of the properties of quadrilaterals and other polygons and the relationships between and among them.
5th Grade
-
Measurement
- The student will become familiar with the units and processes of measurement in order to use a variety of tools, techniques, and formulas to determine and to estimate measurements in mathematical and real-world problems.
6th Grade
-
Measurement
- Content Standard 4.0 The student will become familiar with the units and processes of measurement in order to use a variety of tools, techniques, and formulas to determine and to estimate measurements in mathematical and real-world problems.
7th Grade
-
Measurement
- The student will become familiar with the units and processes of measurement in order to use a variety of tools, techniques, and formulas to determine and to estimate measurements in mathematical and real-world problems.
8th Grade
-
Measurement
- The student will become familiar with the units and processes of measurement in order to use a variety of tools, techniques, and formulas to determine and to estimate measurements in mathematical and real-world problems.
4th Grade
-
Measurement
- The student will become familiar with the units and processes of measurement in order to use a variety of tools, techniques, and formulas to determine and to estimate measurements in mathematical and real-world problems.
Grade 4
-
Measurement
- 11. The student applies measurement concepts. The student is expected to estimate and measure to solve problems involving length (including perimeter) and area. The student uses measurement tools to measure capacity/volume and weight/mass.
Grade 5
-
Measurement
- 10. The student applies measurement concepts involving length (including perimeter), area, capacity/volume, and weight/mass to solve problems.
7th Grade
-
Measurement
- 7.7b The student, given appropriate dimensions, will apply perimeter and area formulas in practical situations.
5th Grade
-
Measurement
- 5.10 The student will differentiate between perimeter, area, and volume and identify whether the application of the concept of perimeter, area, or volume is appropriate for a given situation.
Be Prepared to
- define and describe the concept of perimeter
- exploration questions.