What is Mixtures?
This activity helps the user understand percentages and mixture problems by working with two piles of colored chips. The user can work in one of four modes: Exploration, Unknown Percent, Unknown Total, or Unknown Pile.
Understanding percents is a foundation for proportional reasoning. We see percents almost everyday: discounted pricing, tax, nutrition information to name just a few. Percents are another form of fractions but often easier to work with because percents are always "out of" 100. In more mathematical terms, the denominator when converting from a percent to a fraction is always 100.
When considering mixture problems, as this activity does, we first work with two sets separately and then consider the percent when the sets are combined. Mixture problems are often found in chemistry when chemicals are diluted in a solution. If the chemist needs to mix two solutions together, then the chemist must be able to determine the amount of chemical in the combined solution before mixing them or determine how much of each solution to use to achieve the desired concentration.
How Do I Use This Activity?
Mixtures allows the user to explore percent problems with two sets of circles. Each set of circles can have both colored and / or uncolored circles. The number of colored circles represents the percent of each pile. The user can select from four modes: exploration, unknown pile, unknown percent, or unknown total.
Controls and Output
In the Exploration mode, the activity lets the user create the piles of circles and determine the number of colored circles in each pile. The user can then combine the piles to see the total percent colored.
In the other modes, the activity presents a set of circles in the first pile, some colored and some uncolored. The activity asks the user to create a second pile of colored and uncolored circles to achieve a set that, when combined, has the desired percent of colored circles.
Use the drop down box to select from the four modes.
The two piles are labeled Pile A and Pile B. In the Exploration mode, beneath each pile are a set of controls allowing the user to add or remove circles, and color or uncolor circles in that pile.

In all of the other modes the user can only control the circles in Pile B.
 Exploration mode the user simply adds circles to each pile and colors them.
Exploration mode the user simply adds circles to each pile and colors them.
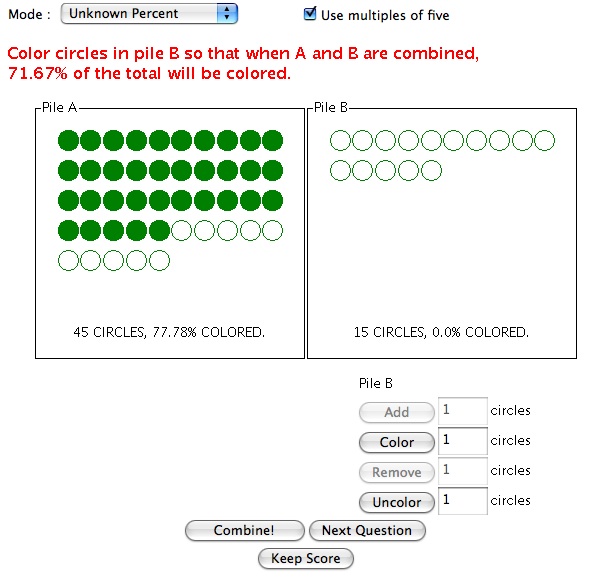
In the Unknown Percent mode the user is given Pile A with uncolored and colored circles and is also given a number of uncolored circles in Pile B. The user is asked to color circles in Pile B such that when the two piles are combined the result will contain a given percent of colored circles.
In the Unknown Total mode the user must create Pile B such that Pile B has a specified percent of circles colored as well as a specified percent of the combined total colored.
In the Unknown Pile mode the user is given Pile A with uncolored and colored circles and must create Pile B by adding uncolored circles and then coloring them such that when the piles are combined the result will contain a given percent of colored circles.
In all modes, to see the resulting values when the piles are combined, simply click the Combine button. Click Next Question to clear the screen and begin again.
When the Use multiples of five check box is checked it forces the activity to choose only the total number of circles in pile A to have a multiple of five.
Scoring
- This activity will automatically record how successful you are at answering the questions. To view the score, press the Show Score button at the bottom of the activity and a pop-up window will appear with the scoreboard. The information in this window is divided into two sections. The statistics for the current question are given in the top half of the window, and the statistics for all questions together are given in the bottom half. To close this pop-up window press the Close button or click back on the main window.
- To pause the scoring, press the Active button at the bottom of the screen and it will change to a Paused button. To resume scoring, press the Paused button.
- To reset the scoreboard, open the scoreboard using the Show Score button and then press the Reset button.
Because this activity randomly generates questions, a feature called Seed Random has been implemented that allows multiple users using different computers to work on the same problem. See Seed Random Help for instructions on using this feature.
Description
Mixtures allows the user to explore percent problems with two sets of circles. Each set of circles can have both colored and / or uncolored circles. The number of colored circles represents the percent of each pile. The user can select from a four modes: Exploration, Unknown Pile, Unknown Percent, or Unknown total.
Place in Mathematics Curriculum
This activity can be used to:
- help students understand and apply algorithms for mixture problems presented in many math textbooks
- explore and create students own mixture problems
Standards Addressed
Grade 6
-
Estimation and Computation
- The student accurately solves problems (including real-world situations).
Grade 7
-
Estimation and Computation
- The student accurately solves problems (including real-world situations).
Grade 8
-
Estimation and Computation
- The student accurately solves problems (including real-world situations).
Grade 9
-
Numeration
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of real numbers.
Grade 10
-
Numeration
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of real numbers.
Sixth Grade
-
Ratios and Proportional Relationships
- Understand ratio concepts and use ratio reasoning to solve problems.
Number and Quantity
-
Quantities
- Reason quantitatively and use units to solve problems.
Grades 6-8
-
Numbers and Operations
- Understand meanings of operations and how they relate to one another
Grades 9-12
-
Algebra
- Represent and analyze mathematical situations and structures using algebraic symbols
Grade 6
-
Number and Operations, Measurement, Geometry, Data Analysis and Probability, Algebra
- COMPETENCY GOAL 1: The learner will understand and compute with rational numbers.
Grade 7
-
Number and Operations, Measurement, Geometry, Data Analysis and Probability, Algebra
- COMPETENCY GOAL 1: The learner will understand and compute with rational numbers.
Technical Mathematics I
-
Number and Operations
- Competency Goal 1: The learner will apply various strategies to solve problems.
6th Grade
-
Numbers and Operations
- The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of the concepts of whole-number percentages, integers, and ratio and rate; the addition and subtraction of fractions; accurate, efficient, and generalizable methods of multiplying and dividing fractions and decimals; and the use of exponential notation to represent whole numbers.
Textbooks Aligned
Grade Seven
-
Comparing and Scaling
- Investigation Two: Comparing by Finding Percents
Book 2
-
Module 5 - Recreation
- Section 3: Percents
Book 3
-
Module 2 - At the Mall
- Section 1: Percent
7th
-
Module 5 - Recreation
- Section 4: Percent
-
Module 8 - Heart of the City
- Section 3: Percent Equations
8th
-
Module 2 - At the Mall
- Section 4: Surveys, Proportions, and Percents
- Section 5: Working with Percents
Book 2
-
Buyer Beware
- Lesson 12: Percent Smorgasbord
Grade 7
-
Cereal Numbers
- Decimals and Percents
Be Prepared to
- explain how to find the resulting percent from combining two sets
- answer questions about finding percents
- give several examples of percents in everyday life