What is Shape Builder?
This activity allows the user to explore area and perimeter by either allowing the computer to randomly draw a shape on a grid or allowing the user to build the shape on the grid.
Surprisingly just because two shapes have the same perimeter does not mean those shapes have the same area. The reverse is also true. Two shapes with the same area do not necessarily have the same perimeter. Examine the two figures below:
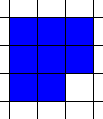
|
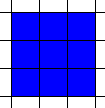
|
| Area=8, Perimeter=12 | Area=9, Perimeter=12 |
Their perimeters are the same but their areas are different! The Shape Builder activity allows you to explore these types of measurement.
One thing worth observing is the fact that shapes will have the same perimeter as long as they have these two characteristics:
1 - Stay within the same rectangular boundaries:
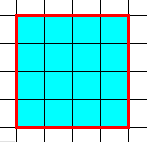
|
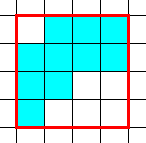
|
| Area=16, Perimeter=16 | Area=10, Perimeter=16 |
2 - Have no "concave" sides:
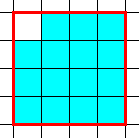
|
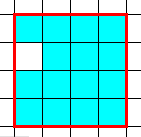
|
| Area=15, Perimeter=16 | Area=15, Perimeter=18 (Concave side) |
How Do I Use This Activity?
This activity allows the user to explore perimeter and area with either rectangular or irregular shapes on a grid. In Auto Draw Mode, the program will randomly generate shapes and ask the user for the perimeter and area of that shape. In Create Shape Mode, the user can build a shape and the program can either display the area and perimeter as the shape is built, or ask the user to enter the answers.
Controls and Output
* There are two modes: Auto Draw Shape and Create Shape. Simply select the radio button next to the mode you want to use.
* While in the Auto Draw Shape mode the program will randomly generate shapes to draw on the grid when you press the New Problem button.
* While in the
Create Shape mode you build your own shapes by clicking on the grid to add squares. These squares can be
moved around by clicking and dragging, or you can remove them by either dragging them off the
grid or clicking on existing stickers.
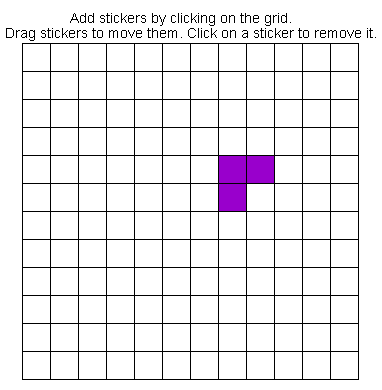
* While in the
Create Shape mode you can choose to either determine the area and perimeter of the shape yourself or allow
the program to show you the answers by checking the boxes in the
Show Answers panel. Note that the
Show Answers panel is unavailable for use in the
Auto Draw Shape mode.

* While in the
Auto Draw Shape mode, you can choose to have the program draw only rectangular shapes by selecting the
Only Draw Rectangular Shapes check box.
* In both modes, you can choose whether or not the grid lines are displayed. You can also choose to display a rectangular outline around the shape. This outline can help you in determining the perimeter of a shape:


* Choose which question types you would like to appear by clicking the checkbox next to Perimeter and Area. Notice, you must select one or the other. You cannot select nothing:
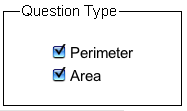
* Click on the New Problem button to got to the next problem.
* Determine the shape's area and / or perimeter (depending on which question types you've
selected) and enter in those values in the corresponding text box. Click the
Check Answer button to see if your answer is correct.

* You can control the size of the shape using the
Adjust Size scroll bar at the bottom of the screen:
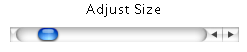
* Use the Reset button to clear the text boxes of their values after inputting answers and complete the same question again.
* The
Compare Area and Perimeters button allows you to keep track of your previous correct answers in order to compare the
corresponding areas to a given perimeter or vice versa. Clicking this button brings up a new
window:
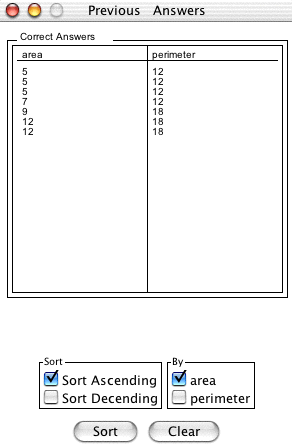 You can sort by either the area or perimeter from least to greatest. To sort by area, make
sure the
area checkbox is selected and to sort by
perimeter, make sure the perimeter checkbox is selected and the click the sort button.
You can sort by either the area or perimeter from least to greatest. To sort by area, make
sure the
area checkbox is selected and to sort by
perimeter, make sure the perimeter checkbox is selected and the click the sort button.
To clear the data and keep the window open, click the clear button.
Scoring
-
This activity will automatically record how successful you are at answering the questions.
To view the score, press the
Show Score button at the bottom of the activity and a pop-up window will appear with the scoreboard.
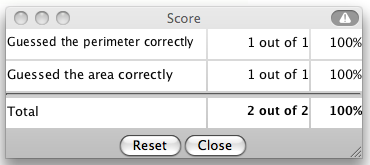
- To close this pop-up window press the Close button or click back on the main window.
- To pause the scoring, press the Active button at the bottom of the screen and it will change to a Paused button. To resume scoring, press the Paused button.
- To reset the scoreboard, open the scoreboard using the Show Score button and then press the Reset button.
Description
This activity allows the user to explore area and perimeter by either allowing the computer to randomly draw a shape on a grid or allowing the user to build the shape on the grid. This activity would work well in mixed ability groups of two or three for about twenty-five minutes if you use the exploration questions and fifteen to twenty minutes otherwise.
Place in Mathematics Curriculum
This activity can be used to:
- illustrate the notion of area
- develop students' visualization skills
- practice students' skills at calculating area
- illustrate shapes of the same perimeter have different areas
Standards Addressed
Grade 3
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates an understanding of geometric relationships.
- The student solves problems using perimeter or area.
- The student demonstrates a conceptual understanding of geometric drawings or constructions.
Grade 4
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates an understanding of geometric relationships.
- The student solves problems using perimeter or area.
- The student demonstrates a conceptual understanding of geometric drawings or constructions.
Grade 5
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates an understanding of geometric relationships.
- The student solves problems (including real-world situations) using perimeter or area.
- The student demonstrates a conceptual understanding of geometric drawings or constructions.
Grade 6
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates an understanding of geometric relationships.
- The student solves problems (including real-world situations) using perimeter, area, or volume.
- The student demonstrates a conceptual understanding of geometric drawings or constructions.
Grade 7
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates an understanding of geometric relationships.
- The student solves problems (including real-world situations).
- The student demonstrates a conceptual understanding of geometric drawings or constructions.
Grade 8
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates an understanding of geometric relationships.
- The student solves problems (including real-world situations).
- The student demonstrates a conceptual understanding of geometric drawings or constructions.
Grade 9
-
Geometry
- The student solves problems (including real-world situations).
Grade 10
-
Geometry
- The student solves problems (including real-world situations).
Grade 4
-
Measurement and Geometry
- 1.0 Students understand perimeter and area
Grade 7
-
Measurement and Geometry
- 2.0 Students compute the perimeter, area, and volume of common geometric objects and use the results to find measures of less common objects. They know how perimeter, area, and volume are affected by changes of scale
Third Grade
-
Geometry
- Reason with shapes and their attributes.
-
Measurement and Data
- Geometric measurement: understand concepts of area and relate area to multiplication and to addition.
- Geometric measurement: recognize perimeter as an attribute of plane figures and distinguish between linear and area measures.
Fifth Grade
-
Geometry
- Classify two-dimensional figures into categories based on their properties.
Sixth Grade
-
Geometry
- Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving area, surface area, and volume.
Seventh Grade
-
Geometry
- Solve real-life and mathematical problems involving angle measure, area, surface area, and volume.
Number and Quantity
-
Quantities
- Reason quantitatively and use units to solve problems.
Grades 3-5
-
Measurement
- Apply appropriate techniques, tools, and formulas to determine measurements
- Understand measurable attributes of objects and the units systems, and processes of measurement
Grades 6-8
-
Geometry
- Analyze characteristics and properties of two- and three-dimensional geometric shapes and develop mathematical arguments about geometric relationships
- Use visualization, spatial reasoning, and geometric modeling to solve problems
-
Measurement
- Apply appropriate techniques, tools, and formulas to determine measurements
Grades 9-12
-
Geometry
- Analyze characteristics and properties of two- and three-dimensional geometric shapes and develop mathematical arguments about geometric relationships
-
Measurement
- Apply appropriate techniques, tools, and formulas to determine measurements
Grade 4
-
Number and Operations, Measurement, Geometry, Data Analysis and Probability, Algebra
- COMPETENCY GOAL 2: The learner will understand and use perimeter and area.
Grade 6
-
Number and Operations, Measurement, Geometry, Data Analysis and Probability, Algebra
- COMPETENCY GOAL 2: The learner will select and use appropriate tools to measure two- and three-dimensional figures.
Grade 8
-
Number and Operations, Measurement, Geometry, Data Analysis and Probability, Algebra
- COMPETENCY GOAL 1: The learner will understand and compute with real numbers.
Introductory Mathematics
-
Geometry and Measurement
- COMPETENCY GOAL 2: The learner will use properties and relationships in geometry and measurement concepts to solve problems.
- COMPETENCY GOAL 2: The learner will understand and use measurement concepts.
-
Number and Operations
- COMPETENCY GOAL 1: The learner will understand and compute with real numbers.
Geometry
-
Geometry and Measurement
- Competency Goal 2: The learner will use geometric and algebraic properties of figures to solve problems and write proofs.
Technical Mathematics I
-
Geometry and Measurement
- Competency Goal 2: The learner will measure and apply geometric concepts to solve problems.
Technical Mathematics II
-
Geometry and Measurement
- Competency Goal 1: The learner will use properties of geometric figures to solve problems.
Integrated Mathematics
-
Geometry and Measurement
- Competency Goal 2: The learner will use properties of geometric figures to solve problems.
Integrated Mathematics III
-
Geometry and Measurement
- Competency Goal 2: The learner will use properties of geometric figures to solve problems.
7th Grade
-
Measurement
- The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of how to use ratio and proportion to solve problems involving scale factors and rates and how to use one-step unit analysis to convert between and within the U.S. Customary
- The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of how to use ratio and proportion to solve problems involving scale factors and rates and how to use one-step unit analysis to convert between and within the U.S. Customary System and the metric system.
8th Grade
-
Measurement
- The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of the proportionality of similar figures; the necessary levels of accuracy and precision in measurement; the use of formulas to determine circumference, perimeter, area, and
- The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of the proportionality of similar figures; the necessary levels of accuracy and precision in measurement; the use of formulas to determine circumference, perimeter, area, and volume; and the use of conversions within and between the U.S. Customary System and the metric system.
5th Grade
-
Measurement
- The student will become familiar with the units and processes of measurement in order to use a variety of tools, techniques, and formulas to determine and to estimate measurements in mathematical and real-world problems.
4th Grade
-
Measurement
- The student will become familiar with the units and processes of measurement in order to use a variety of tools, techniques, and formulas to determine and to estimate measurements in mathematical and real-world problems.
Grade 4
-
Measurement
- 11. The student applies measurement concepts. The student is expected to estimate and measure to solve problems involving length (including perimeter) and area. The student uses measurement tools to measure capacity/volume and weight/mass.
Grade 5
-
Measurement
- 10. The student applies measurement concepts involving length (including perimeter), area, capacity/volume, and weight/mass to solve problems.
Textbooks Aligned
Grade Six
-
Covering and Surrounding
- Investigation One: Measuring Perimeter and Area
- Investigation Three: Constant Area, Changing Perimeter
- Investigation Four: Constant Perimeter, Changing Area
Book 3
-
Module 1 - Amazing Feats, Facts and Fictions
- Section 6: Area, Perimeter
-
Module 3 - The Mystery of Blacktail Canyon
- Section 1: Length, Area
-
Module 6 - Architects and Engineers
- Section 6: Perimeter and Area of Similar Figures
Book 1
-
Designing Spaces
- Lesson 1: Planning and Building a Modular House
- Lesson 2: Seeing Around the Corners
- Lesson 3: Seeing All Possibilities
- Lesson 4: Picture This
-
Patterns in Numbers and Shapes
- Lesson 5: Tiling Garden Beds
- Lesson 6: Chocolates by the Box
Book 2
-
From the Ground Up
- Lesson 1: Designing a Floor Plan
-
Getting In Shape
- Lesson 11: Around the Area
Grade 6
-
Reallotment
- Estimating Area
- Perimeter
Be Prepared to
- Discuss and demonstrate why shapes can have the same areas but different perimeters.
- Discuss and demonstrate why shapes can have the same perimeters but different areas.
- Emphasize the difference between the units to measure perimeter (linear) and area (square).