What is Triangle Explorer?
This applet allows users to study the nature of triangles and their area. It draws random triangles on a Cartesian coordinate system. The user can determine the area of the triangle using his or her preferred method. After the calculated area is entered into the input box, the applet will tell the user if s/he has the correct answer. Hints are available to help the user find the correct answer, if necessary.
How Do I Use This Activity?
This applet allows users to study the nature of triangles and their area.
Controls and Output
The object of this activity is to improve the user's understanding of the area of a triangle and to improve the skills needed for calculating this area. The user may use any appropriate method for finding the area of a triangle, and once the area is entered, the applet will respond with "Correct," or "Incorrect. Try Again."
There is more than one way, of course, to find the area of a triangle. If the user is unsure how to approach the problem, clicking the Give Hint button may prove to be helpful.

The hint button draws additional lines which may allow the user to visualize the problem in a different way.
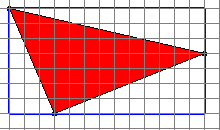
The user can then input the calculated area into the box and check the answer by clicking the Check Answer button.

The program will then tell the user if their answer is correct or incorrect. If the answer is incorrect, redo the calculations to check for errors or try a different method for finding the area.
When the user has found the correct area of a given triangle, a new triangle may be obtained by clicking on the New Traingle button.

As the user becomes more skilled at calculating the area of a triangle, more difficult problems can be obtained using the pull-down menu at the top of the applet. Users may choose from level 1, level 2, or level 3 problems.
Scoring
-
This activity will automatically record how successful you are at answering the questions.
To view the score, press the
Show Score button at the bottom of the activity and a pop-up window will appear with the scoreboard.
- To close this pop-up window press the Close button or click back on the main window.
- To pause the scoring, press the Active button at the bottom of the screen and it will change to a Paused button. To resume scoring, press the Paused button.
- To reset the scoreboard, open the scoreboard using the Show Score button and then press the Reset button.
Description
This applet allows the user to study the nature of triangles and their area. This activity would work well in same ability groups of two or three for about twenty-five to thirty minutes if you use the exploration questions and fifteen minutes otherwise.
Place in Mathematics Curriculum
This activity can be used to:
- introduce the concept of area
- explore different types of triangles
- discuss problem solving strategies
Standards Addressed
Grade 6
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates an understanding of geometric relationships.
- The student solves problems (including real-world situations) using perimeter, area, or volume.
- The student demonstrates a conceptual understanding of geometric drawings or constructions.
Grade 7
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates an understanding of geometric relationships.
- The student solves problems (including real-world situations).
- The student demonstrates a conceptual understanding of geometric drawings or constructions.
Grade 8
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates an understanding of geometric relationships.
- The student solves problems (including real-world situations).
- The student demonstrates a conceptual understanding of geometric drawings or constructions.
Grade 9
-
Geometry
- The student solves problems (including real-world situations).
Grade 10
-
Geometry
- The student solves problems (including real-world situations).
Number and Quantity
-
Quantities
- Reason quantitatively and use units to solve problems.
Grades 3-5
-
Measurement
- Apply appropriate techniques, tools, and formulas to determine measurements
Grades 6-8
-
Geometry
- Specify locations and describe spatial relationships using coordinate geometry and other representational systems
-
Measurement
- Apply appropriate techniques, tools, and formulas to determine measurements
Grades 9-12
-
Geometry
- Analyze characteristics and properties of two- and three-dimensional geometric shapes and develop mathematical arguments about geometric relationships
- Specify locations and describe spatial relationships using coordinate geometry and other representational systems
-
Measurement
- Apply appropriate techniques, tools, and formulas to determine measurements
Grade 6
-
Number and Operations, Measurement, Geometry, Data Analysis and Probability, Algebra
- COMPETENCY GOAL 2: The learner will select and use appropriate tools to measure two- and three-dimensional figures.
- COMPETENCY GOAL 3: The learner will understand and use properties and relationships of geometric figures in the coordinate plane.
Grade 8
-
Number and Operations, Measurement, Geometry, Data Analysis and Probability, Algebra
- COMPETENCY GOAL 3: The learner will understand and use properties and relationships in geometry.
Introductory Mathematics
-
Data Analysis and Probability
- COMPETENCY GOAL 3: The learner will understand and use properties and relationships in geometry.
-
Geometry and Measurement
- COMPETENCY GOAL 2: The learner will use properties and relationships in geometry and measurement concepts to solve problems.
Geometry
-
Geometry and Measurement
- Competency Goal 2: The learner will use geometric and algebraic properties of figures to solve problems and write proofs.
Technical Mathematics I
-
Geometry and Measurement
- Competency Goal 2: The learner will measure and apply geometric concepts to solve problems.
Technical Mathematics II
-
Geometry and Measurement
- Competency Goal 1: The learner will use properties of geometric figures to solve problems.
Integrated Mathematics
-
Geometry and Measurement
- Competency Goal 2: The learner will use properties of geometric figures to solve problems.
Integrated Mathematics II
-
Geometry and Measurement
- Competency Goal 2: The learner will describe geometric figures in the coordinate plane algebraically.
Integrated Mathematics III
-
Geometry and Measurement
- Competency Goal 2: The learner will use properties of geometric figures to solve problems.
5th Grade
-
Measurement
- The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of the units and systems of measurement and the application of tools and formulas to determine measurements.
4th Grade
-
Measurement
- Standard 4-5: The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of elapsed time; conversions within the U.S. Customary System; and accurate, efficient, and generalizable methods of determining area.
7th Grade
-
Geometry
- The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of proportional reasoning, tessellations, the use of geometric properties to make deductive arguments. the results of the intersection of geometric shapes in a plane, and the
8th Grade
-
Measurement
- The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of the proportionality of similar figures; the necessary levels of accuracy and precision in measurement; the use of formulas to determine circumference, perimeter, area, and
Geometry
-
Geometry
- Standard G-3: The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of the properties and special segments of triangles and the relationships between and among triangles.
8th Grade
-
Geometry
- 8.10 The student will
Secondary
-
Algebra II
- AII.5
- AII.16
Textbooks Aligned
Grade Six
-
Covering and Surrounding
- Investigation Six: Measuring Triangles
6th
-
Module 5 - Creating Things
- Section 5: Area
Be Prepared to
- explain and give examples of right triangles
- explain and give examples of how to calculate the area of a right triangle
- explain and give examples of how to calculate the area of a triangle that is not a right triangle