What is Squaring the Triangle?
This applet allows users to explore right triangles and the Pythagorean Theorem. The applet can also be used to explore the angle measurements of triangles.
Pythagoras, to whom the theorem owes its name, was a Greek philosopher and scientist. The theorem that he is credited with states the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
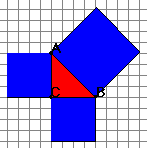
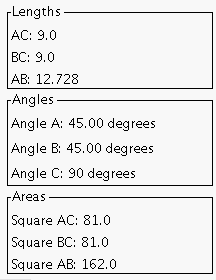
In order for the user to study the relationship involved in the Pythagorean Theorem, this applet draws a square against each side of the triangle. As the user adjusts the length of a side of the triangle, the squares adjust accordingly. Descriptive information about the length of each side, the measure of each angle, and the area of each square is provided on the applet.
How Do I Use This Activity?
This applet allows users to explore right triangles and the Pythagorean Theorem. The applet can also be used to explore the angle measurements of triangles.
Object of the activity The object of this activity is to develop an understanding of the Pythagorean Theorem. The applet displays a right triangle with a square against each side. Each square has sides that are equal in length to the side of the triangle it is against. By adjusting the lengths of the sides of the triangle, the user can visually experience the Pythagorean Theorem.
Controls and Output
-
By adjusting the scrollbars the user can change the lengths of the bases of the red
triangle:

-
Observe how the triangle changes and how the squares change in area. What is the
relationship between the squares?
-
The information to the left of the applet is provided to help the user form an
understanding of the relationship of the areas of the squares and the lengths of the
sides. The user may also make discoveries about the nature of angles in triangles.
Description
This activity allows the user to investigate the fundamental ideas behind the Pythagorean theorem and the nature of triangles. This activity would work well in groups of two for about fifteen to twenty minutes if you use the exploration questions and five to ten minutes otherwise.
Place in Mathematics Curriculum
This activity can be used to:
- introduce the Pythagorean Theorem
- explore the concept of area
- explore the nature of the angles in triangles
Standards Addressed
Grade 6
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates an understanding of geometric relationships.
- The student solves problems (including real-world situations) using perimeter, area, or volume.
- The student demonstrates a conceptual understanding of geometric drawings or constructions.
Grade 7
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates an understanding of geometric relationships.
- The student solves problems (including real-world situations).
- The student demonstrates a conceptual understanding of geometric drawings or constructions.
Grade 8
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates an understanding of geometric relationships.
- The student solves problems (including real-world situations).
- The student demonstrates a conceptual understanding of geometric drawings or constructions.
Grade 9
-
Geometry
- The student solves problems (including real-world situations).
Grade 10
-
Geometry
- The student solves problems (including real-world situations).
Grade 7
-
Measurement and Geometry
- 3.0 Students know the Pythagorean theorem and deepen their understanding of plane and solid geometric shapes by constructing figures that meet given conditions and by identifying attributes of figures
Eighth Grade
-
Geometry
- Understand and apply the Pythagorean Theorem.
Geometry
-
Similarity, Right Triangles, and Trigonometry
- Define trigonometric ratios and solve problems involving right triangles
Grades 6-8
-
Geometry
- Use visualization, spatial reasoning, and geometric modeling to solve problems
Grades 9-12
-
Geometry
- Analyze characteristics and properties of two- and three-dimensional geometric shapes and develop mathematical arguments about geometric relationships
Grade 8
-
Number and Operations, Measurement, Geometry, Data Analysis and Probability, Algebra
- COMPETENCY GOAL 3: The learner will understand and use properties and relationships in geometry.
Introductory Mathematics
-
Data Analysis and Probability
- COMPETENCY GOAL 3: The learner will understand and use properties and relationships in geometry.
-
Geometry and Measurement
- COMPETENCY GOAL 2: The learner will use properties and relationships in geometry and measurement concepts to solve problems.
- COMPETENCY GOAL 2: The learner will understand and use measurement concepts.
Geometry
-
Geometry and Measurement
- Competency Goal 2: The learner will use geometric and algebraic properties of figures to solve problems and write proofs.
Technical Mathematics I
-
Geometry and Measurement
- Competency Goal 2: The learner will measure and apply geometric concepts to solve problems.
Technical Mathematics II
-
Geometry and Measurement
- Competency Goal 1: The learner will use properties of geometric figures to solve problems.
Discrete Mathematics
-
Algebra
- Competency Goal 3: The learner will describe and use recursively-defined relationships to solve problems.
Integrated Mathematics III
-
Geometry and Measurement
- Competency Goal 2: The learner will use properties of geometric figures to solve problems.
7th Grade
-
Geometry
- The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of proportional reasoning, tessellations, the use of geometric properties to make deductive arguments. the results of the intersection of geometric shapes in a plane, and the
- The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of proportional reasoning, tessellations, the use of geometric properties to make deductive arguments. the results of the intersection of geometric shapes in a plane, and the relationships among angles formed when a transversal intersects two parallel lines.
8th Grade
-
Measurement
- The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of the proportionality of similar figures; the necessary levels of accuracy and precision in measurement; the use of formulas to determine circumference, perimeter, area, and
- The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of the proportionality of similar figures; the necessary levels of accuracy and precision in measurement; the use of formulas to determine circumference, perimeter, area, and volume; and the use of conversions within and between the U.S. Customary System and the metric system.
Geometry
-
Geometry
- Standard G-3: The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of the properties and special segments of triangles and the relationships between and among triangles.
7th Grade
-
Patterns, Functions, and Algebra
- 7.22 The student will
- 7.22a The student will solve one-step linear equations and inequalities in one variable with strategies involving inverse operations and integers, using concrete materials, pictorial representations, and paper and pencil
8th Grade
-
Computation and Estimation
- 8.5 The student, given a whole number from 0 to 100, will identify it as a perfect square or find the two consecutive whole numbers between which the square root lies.
- 8.5 The student, given a whole number from 0 to 100, will identify it as a perfect square or
-
Geometry
- 8.10a The student will verify the Pythagorean Theorem, using diagrams, concrete materials, and measurement; and
- 8.10 The student will
-
Patterns, Functions, and Algebra
- 8.17 The student will create and solve problems, using proportions, formulas, and functions.
6th Grade
-
Measurement
- 6.13a The student will estimate angle measures, using 45°, 90°, and 180° as referents, and use the appropriate tools to measure the given angles
- 6.13a The student will estimate angle measures, using 45°, 90°, and 180° as referents, and use the appropriate tools to measure the given angles
Secondary
-
Algebra II
- AII.05 The student will identify and factor completely polynomials representing the difference of squares, perfect square trinomials, the sum and difference of cubes, and general trinomials.
- AII.5
Textbooks Aligned
Grade Eight
-
Looking for Pythagoras
- Investigation Three: The Pythagorean Theorem
Book 1
-
Module 1 - Tools for Success
- Section 2: Sides of a Triangle
- Section 2: Angles of a Triangle
- Section 6: Improve your problem solving
-
Module 7 - Wonders of the World
- Section 1: Customary Units for Area
- Section 1: Area of a Parallelogram, Area of a Triangle
Book 2
-
Module 6 - Flights of Fancy
- Section 4: Angles formed by a Transversal
- Section 4: Angles in Triangles and Parallelograms
Book 3
-
Module 4 - Patterns and Discoveries
- Section 5: Angles in Polygons
- Section 6: Triangle Side Length Relationships
8th
-
Module 5 - Architects and Engineers
- Section 3: Working with Triangles
Book 3
-
Mathematics of Motion
- Lesson 3: Reporting Live From the Parade
- Lesson 4: The Parade Continues
Grade 8
-
Going the Distance
- Pythagorean Theorem
-
Patterns and Figures
- Triangular Numbers
- Pascal's Triangle
-
Triangles and Patchwork
- Similarity
- Similar Triangles
Grade 7
-
Triangles and Beyond
- Constructing Triangles
- Similarity
Be Prepared to
- give implicit directions on what they are to do. For example "Today we are going to play with the Squaring the Triangle applet. We will be looking for patterns in the area of the squares, the angles, ... and we are going to see what we can discover."
- discuss the Pythagorean Theorem and define hypotenuse