Abstract
It is necessary for fourth and fifth grade students to be able to convert between fractions, decimals, and percents. Much of this learning must be done through repetition and practice once students begin to grasp the concept. This lesson provides a way for students to practice this concept.
Objectives
Upon completion of this lesson, students will:
- practice naming and converting between fractions, decimals, and percents.
Standards Addressed
Grade 3
-
Numeration
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of simple fractions with denominators 2, 3, 4, or 10.
Grade 4
-
Numeration
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of fractions with denominators 2 through 12.
Grade 5
-
Numeration
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of positive fractions with denominators 1 through 12 and 100 with proper and mixed numbers and benchmark percents (10%, 25%, 50%, 75%, 100%).
Grade 6
-
Numeration
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of fractions (proper or mixed numbers), decimals, percents (whole number), or integers.
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of fractions, mixed numbers, or percents.
Grade 7
-
Numeration
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of rational numbers (fractions, decimals, percents, or integers).
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of positive fractions, decimals, or percents.
Grade 8
-
Numeration
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of real numbers.
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of rational numbers (fractions, decimals, or percents including integers).
Grade 9
-
Estimation and Computation
- The student accurately solves problems (including real-world situations).
-
Numeration
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of real numbers.
Grade 10
-
Estimation and Computation
- The student accurately solves problems (including real-world situations).
-
Numeration
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of real numbers.
Third Grade
-
Number and Operations-Fractions
- Develop understanding of fractions as numbers.
Fourth Grade
-
Number and Operations-Fractions
- Extend understanding of fraction equivalence and ordering.
- Build fractions from unit fractions by applying and extending previous understandings of operations on whole numbers.
Sixth Grade
-
The Number System
- Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication and division to divide fractions by fractions.
Grades 3-5
-
Numbers and Operations
- Compute fluently and make reasonable estimates
Grades 6-8
-
Numbers and Operations
- Compute fluently and make reasonable estimates
Grade 6
-
Number and Operations, Measurement, Geometry, Data Analysis and Probability, Algebra
- COMPETENCY GOAL 1: The learner will understand and compute with rational numbers.
Grade 7
-
Number and Operations, Measurement, Geometry, Data Analysis and Probability, Algebra
- COMPETENCY GOAL 1: The learner will understand and compute with rational numbers.
Student Prerequisites
-
Arithmetic:
Students must be able to:
- add, subtract, multiply, and divide whole numbers.
-
Technological:
Students must be able to:
- perform basic mouse manipulations such as point, click and drag.
Teacher Preparation
- access to a browser
- pencil and paper
Key Terms
decimal
Short for the term "decimal fraction", a decimal is another way to represent fractional numbers. The decimal uses place value to express the value of a number as opposed to a fraction that uses a numerator and denominator.
decimal number
A fraction where the denominator is a power of ten and is therefore expressed using a decimal point. For example: 0.37 is the decimal equivalent of 37/100
fraction
A rational number of the form a/b where a is called the numerator and b is called the denominator
percent
A ratio that compares a number to one hundred. The symbol for percent is %
Lesson Outline
-
Focus and Review
Get the students to think about fractions by asking them to think of things they needed to share by splitting a single object into parts. Possibly give the example of a pizza or a piece of paper.
-
Objectives
Today, class, we are going to use the computers to help practice our skills working with fractions, decimals, and percents.
-
Teacher Input
Give students several examples of fractions, decimals and percents used in the real world. Examples such as sharing a pizza, a ruler, measures on bottles or cans for decimals, or food labels for percents. Discuss with the students that these are all representations of the same thing. A fraction can be expressed as a decimal or as a percent and vice versa.
-
Guided Practice
Give the students time so they may try to solve the problems on the worksheet by themselves. Once the students have had enough time to solve the problems, have them check their fraction to decimal conversion answers using the Fraction Converter applet.
-
Independent Practice
Once the students have opened the Pie Chart applet, tell them to adjust the applet settings so that the pie chart only has two sections. After all of the settings are correctly adjusted, have the students try to replicate their answers from the worksheet using the two sections. It may be helpful to remind your students the sum of the two sections must equal 100. For example:
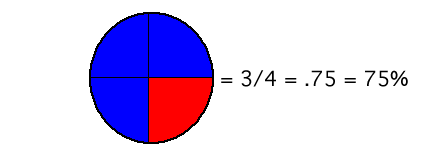
You would have the students enter 75% as the percentage for one portion of the circle and 25% for the other. Then the students would compare the circle they colored with the one colored by the Pie chart applet to make sure they look similar. Once the students have completed the worksheet, they can choose partners and play the Fraction Four applet. Be sure you tell them to set the "problem type" in the Fraction Four applet to "fractions, decimals, and percents".
-
Closure
Have students come to the board and share one of their responses to the worksheet.