What is Comparison Estimator?
This activity allows the user to understand the estimation process by comparing two objects. Students can choose to compare the length of two lines, the area of two shapes, or the number of objects on each side.
When the two things you are comparing are viewed at the same scale, it is often easier to identify which is bigger, longer, or greater. If their scales are different, however, you can estimate one, then the other, and compare those amounts.
Estimation skills are crucial in day to day life. Being able to estimate well can help in reading maps, making economical purchases, determining how much tip to leave for a meal, telling a friend an accurate time where you can meet them someplace after finishing your chores, and many other daily tasks. Estimation is a useful tool to get a general idea about a quantity or a size when an exact answer is not necessary.
How Do I Use This Activity?
This activity allows the user to practice estimation skills. The user must compare two quantities (which may be the number of objects in each of two sets, the lengths of two curves, or the area of two shapes) by estimating.
Controls and Output
- This activity asks you to make three different types of estimations: counting, length, and area. In the center of the activity there are two pictures. For counting problems, the pictures show two groups of objects. You have to estimate whether the number of objects on the left is greater than or less than the number of objects on the right. For length problems, the pictures show two curves. Again, you have to estimate whether the length of the curve on the left is greater than or less than the length of the curve on the right. For area problems, the pictures show two shapes and the same question applies to the areas of the two shapes.
-
When the problem is a length or area problem, you will be given a scale in the upper
left-hand part of the picture. The length scale looks like this:
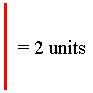
This tells you that the length of the line on the screen is equal to 2 units. You should use these units to estimate the length of the curve. The area scale looks like this:
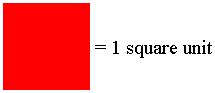
This tells you that the area of the square on the screen is equal to 1 square unit. You should use these units to estimate the area of the shape.
-
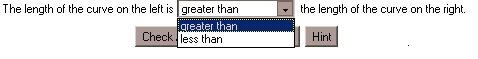
To answer a question, choose from the pull-down menu the phrase that best completes the
sentence. You can choose "greater than" or "less than." Once you've selected your answer,
click the
Check Answer button to see if it is correct.
-
If you need help, click the
Hint button. This will display a grid over the picture. You can use this grid as an aid to
your estimation.

-
To go to the next problem, click the
Next Problem button:
-
There are several settings you can control in this activity. You can set the type of
problems you see by picking a problem from the
Problem Type pull-down menu. If you choose "Random," the activity will give you random problems that
may be counting, length, or area problems. If you choose any of the other three options,
you will only get problems of that type.
-
You can choose from two levels: level 1 and level 2.
- This activity will automatically record how successful you are at answering the questions. To view the score, press the Show Score button at the bottom of the activity and a pop-up window will appear with the scoreboard. To close this pop-up window press the Close button or click back on the main window.
- To pause the scoring, press the Active button at the bottom of the screen and it will change to a Paused button. To resume scoring, press the Paused button.
- To reset the scoreboard, open the scoreboard using the Show Score button and then press the Reset button.
Because this activity randomly generates questions, a feature called Seed Random has been implemented that allows multiple users using different computers to work on the same problem. See Seed Random Help for instructions on using this feature.
Description
This activity allows the user to compare two quantities (which may be the number of objects in each of two sets, the lengths of two curves, or the area of two shapes) by estimating. This activity would work well in small groups of 2-4 for about 20-25 minutes if you use the exploration questions and 10-15 minutes otherwise.
Place in Mathematics Curriculum
This activity can be used to:
- Introduce students to the uses and limits of estimation
- Reinforce basic concepts in geometry such as simple shapes and area
- Show students the importance of comparing scales on different graphical displays
Standards Addressed
Grade 3
-
Estimation and Computation
- The student determines reasonable answers to real-life situations, paper/pencil computations, or calculator results.
- The student accurately solves problems (including real-world situations).
-
Numeration
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of whole numbers up to one thousand.
Grade 4
-
Estimation and Computation
- The student determines reasonable answers to real-life situations, paper/pencil computations, or calculator results.
- The student accurately solves problems (including real-world situations).
-
Numeration
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of whole numbers to ten thousands.
Grade 5
-
Estimation and Computation
- The student determines reasonable answers to real-life situations, paper/pencil computations, or calculator results.
- The student accurately solves problems (including real-world situations).
-
Numeration
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of whole numbers to millions.
Grade 6
-
Estimation and Computation
- The student determines reasonable answers to real-life situations, paper/pencil computations, or calculator results.
-
Measurement
- The student demonstrates understanding of measurable attributes.
Grade 7
-
Estimation and Computation
- The student solves problems (including real-world situations) using estimation.
Grade 8
-
Estimation and Computation
- The student solves problems (including real-world situations) using estimation.
Grade 9
-
Estimation and Computation
- The student solves problems (including real-world situations) using estimation.
-
Numeration
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of real numbers.
Grade 10
-
Estimation and Computation
- The student solves problems (including real-world situations) using estimation.
-
Numeration
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of real numbers.
Number and Quantity
-
Quantities
- Reason quantitatively and use units to solve problems.
Grades 3-5
-
Measurement
- Apply appropriate techniques, tools, and formulas to determine measurements
Grades 6-8
-
Measurement
- Apply appropriate techniques, tools, and formulas to determine measurements
Grade 6
-
Number and Operations, Measurement, Geometry, Data Analysis and Probability, Algebra
- COMPETENCY GOAL 2: The learner will select and use appropriate tools to measure two- and three-dimensional figures.
Technical Mathematics I
-
Number and Operations
- Competency Goal 1: The learner will apply various strategies to solve problems.
Advanced Functions and Modeling
-
Data Analysis and Probability
- Competency Goal 1: The learner will analyze data and apply probability concepts to solve problems.
3rd Grade
-
Measurement
- The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of length, time, weight, and liquid volume measurements; the relationships between systems of measure; accurate, efficient, and generalizable methods of determining the perim
- The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of length, time, weight, and liquid volume measurements; the relationships between systems of measure; accurate, efficient, and generalizable methods of determining the perimeters of polygons; and the values and combinations of coins required to make change.
5th Grade
-
Measurement
- The student will become familiar with the units and processes of measurement in order to use a variety of tools, techniques, and formulas to determine and to estimate measurements in mathematical and real-world problems.
3rd Grade
-
Measurement
- Content Standard 4.0 The student will become familiar with the units and processes of measurement in order to use a variety of tools, techniques, and formulas to determine and to estimate measurements in mathematical and real-world problems.
4th Grade
-
Measurement
- The student will become familiar with the units and processes of measurement in order to use a variety of tools, techniques, and formulas to determine and to estimate measurements in mathematical and real-world problems.
3rd Grade
-
Number and Number Sense
- 3.3 The student will compare two whole numbers between 0 and 9,999, using symbols (>, <, or = ) and words (greater than, less than, or equal to).
- 3.03 The student will compare two whole numbers between 0 and 9,999, using symbols (>, <, or =) and words (greater than, less than, or equal to)
4th Grade
-
Computation and Estimation
- 4.5 The student will estimate whole-number sums and differences and describe the method of estimation. Students will refine estimates, using terms such as closer to, between, and a little more than.
5th Grade
-
Measurement
- 5.11a The student will choose an appropriate measuring device and unit of measure to solve problems involving measurement of length - part of an inch (1/2, 1/4, and 1/8), inches, feet, yards, miles, millimeters, centimeters, meters, and kilometers
- 5.11a The student will choose an appropriate measuring device and unit of measure to solve problems involving measurement of length — part of an inch (1/2, 1/4, and 1/8), inches, feet, yards, miles, millimeters, centimeters, meters, and kilometers
6th Grade
-
Measurement
- 6.10 The student will estimate and then determine length, weight/mass, area, and liquid volume/capacity, using standard and nonstandard units of measure.
-
Number and Number Sense
- 6.2 The student will describe and compare two sets of data, using ratios, and will use appropriate notations, such as a/b, a to b, and a:b.
Be Prepared to
- Encourage the students to estimate rather than measure or count
- Discuss how estimation is not as accurate as measurement
- Explain the difference between close, really close, and almost perfect (almost perfect is the mostaccurate)
- Suggest that the students eventually increase the difficulty level