What is Estimator Quiz?
This activity allows a student to practice answering questions using estimation. Users can choose to estimate addition, multiplication, and percentage problems.
One method of estimation is to round the numbers first, then complete the operations. To round, think about making "easy" numbers. With larger numbers, this probably means rounding to hundreds, or even thousands depending on the size of the numbers. With smaller numbers, rounding to hundreds or tens could give you answers that are not close to the correct answers. If the numbers are less than one hundred apart, rounding to the nearest hundred will probably not be the best method. Instead, consider rounding to the nearest ten or even five.
Estimation skills are crucial in day to day life. Being able to estimate well can help in reading maps, making economical purchases, determining how much tip to leave for a meal, telling a friend an accurate time where you can meet them someplace after finishing your chores, and many other daily tasks.
How Do I Use This Activity?
This activity allows the user to practice estimating the results of addition, multiplication, and percentage problems.
In this applet, questions are categorized by a combination of level (which determines the difficulty) and by types of problems listed. For more information on how questions are generated and what each level and problem type means, see Question Types for Estimator Quiz and Estimator Four.
Controls and Output
-
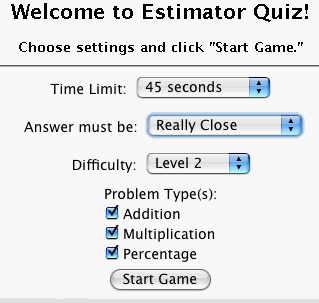
Before you start the game, you can set several options. You can choose how much time each
player will have to answer the questions. You can set the tolerance, which determines how
close your answer must be to the actual answer to be counted correct. You can choose the
problem difficulty (Level 1, Level 2, Level 3). You can also select the types of
estimation problems you want to see. Once you have all the settings as you want them,
click the
Start Game button.
-
After clicking the
Start Game button, a new screen appears. Towards the left of the screen is a table that lists the
types of questions selected along with the difficulty level.

-
Enter your answer into the answer textbox:

-
After you have entered your answer, you need to click on the
 button to find out if you are correct. Since this is an
estimation activity, your answer doesn't have to be exactly right. It can be either above or below
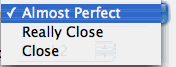
the actual answer, as long as it is within the tolerance selected from the
Answer must be menu in the starting screen.
button to find out if you are correct. Since this is an
estimation activity, your answer doesn't have to be exactly right. It can be either above or below
the actual answer, as long as it is within the tolerance selected from the
Answer must be menu in the starting screen.
-
You have a limited amount of time to answer. The
timer on the right-hand side of the board shows how much time you have left. Once the timer
turns all gray, the time is up.

-
If you want to restart the game, you can do so by clicking on the
New Game button:

- This activity will automatically record how successful you are at answering the questions. To view the score, press the Show Score button at the bottom of the activity and a pop-up window will appear with the scoreboard. To close this pop-up window press the Close button or click back on the main window.
- To pause the scoring, press the Active button at the bottom of the screen and it will change to a Paused button. To resume scoring, press the Paused button.
- To reset the scoreboard, open the scoreboard using the Show Score button and then press the Reset button.
Description
This activity allows a student to practice answering questions with estimation. Users can choose to estimate addition, multiplication, and percentage problems. This activity would work well with students working individually for about 25-30 minutes if you use the exploration questions and 15-20 minutes otherwise.
Place in Mathematics Curriculum
This activity can be used to:
- Introduce students to the uses and limits of estimation
- Reinforce understanding of addition, multiplication, and percentage problems involving largenumbers
Standards Addressed
Grade 3
-
Estimation and Computation
- The student determines reasonable answers to real-life situations, paper/pencil computations, or calculator results.
- The student accurately solves problems (including real-world situations).
-
Numeration
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of whole numbers up to one thousand.
Grade 4
-
Estimation and Computation
- The student determines reasonable answers to real-life situations, paper/pencil computations, or calculator results.
- The student accurately solves problems (including real-world situations).
-
Numeration
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of whole numbers to ten thousands.
Grade 5
-
Estimation and Computation
- The student determines reasonable answers to real-life situations, paper/pencil computations, or calculator results.
- The student accurately solves problems (including real-world situations).
-
Numeration
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of whole numbers to millions.
Grade 6
-
Estimation and Computation
- The student determines reasonable answers to real-life situations, paper/pencil computations, or calculator results.
-
Measurement
- The student demonstrates understanding of measurable attributes.
Grade 7
-
Estimation and Computation
- The student solves problems (including real-world situations) using estimation.
Grade 8
-
Estimation and Computation
- The student solves problems (including real-world situations) using estimation.
Grade 9
-
Estimation and Computation
- The student solves problems (including real-world situations) using estimation.
-
Numeration
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of real numbers.
Grade 10
-
Estimation and Computation
- The student solves problems (including real-world situations) using estimation.
-
Numeration
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of real numbers.
Number and Quantity
-
Quantities
- Reason quantitatively and use units to solve problems.
Grades 3-5
-
Numbers and Operations
- Compute fluently and make reasonable estimates
Grades 6-8
-
Numbers and Operations
- Compute fluently and make reasonable estimates
Grades 9-12
-
Numbers and Operations
- Compute fluently and make reasonable estimates
Technical Mathematics I
-
Number and Operations
- Competency Goal 1: The learner will apply various strategies to solve problems.
5th Grade
-
Number and Operation
- The student will develop number and operation sense needed to represent numbers and number relationships verbally, symbolically, and graphically and to compute fluently and make reasonable estimates in problem solving.
Grade 3
-
Number, Operation, and Quantitative Reasoning
- 5. The student estimates to determine reasonable results.
Grade 4
-
Number, Operation, and Quantitative Reasoning
- 5. The student estimates to determine reasonable results.
Grade 5
-
Number, Operation, and Quantitative Reasoning
- 4. The student estimates to determine reasonable results. The student is expected to use strategies, including rounding and compatible numbers to estimate solutions to addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division problems.
Be Prepared to
- Encourage the students to estimate rather than trying to compute the values exactly
- Discuss how estimation is not as accurate as calculation
- Explain the difference between close, really close, and almost perfect (almost perfect is the mostaccurate)
- Suggest that the students eventually increase the difficulty level