What is Fraction Sorter?
This activity allows the user to enhance their skills working with fractions by first making fractions by cutting squares or circles into parts (this correlates with the denominator) and then coloring in the correct portions (this correlates to the numerator). They then place these fractions in order from least to greatest.
Fractions are used often in mathematics and in day to day life. Any time you cut a whole into equal size parts you are using fractions, such as cutting a pizza or a cake, or determining how many questions you got correct on a test.
This activity is an excellent way to learn about what fractions are and practice with them in order to help you understand the correlation between their representation as numerals and their value on the number line.
How Do I Use This Activity?
This activity allows the user to develop his/her understanding of fractions and practice comparing them.
Controls and Output
This activity requires you to build two or more fractions and then order them from smallest to largest.
-
First, select whether you wish to work with circles or squares. Next, change the number of
shapes you wish to sort.

- You may use the "New" button at any time to start over with a new set of fractions.
-
Use the Sec+ and Sec- buttons above the circles to divide your shape into sections. If you
are using squares, then use the Row-, Row+, and Col-, Col+ buttons to create sections.
 These sections represent the denominator of the fraction. Once you have the correct
number of sections, click in the appropriate number of those sections to represent the
numerator of the fraction.
These sections represent the denominator of the fraction. Once you have the correct
number of sections, click in the appropriate number of those sections to represent the
numerator of the fraction.
-
When you believe you have correctly represented the fraction, click on the "Check" button
above the circle to see if you are right.
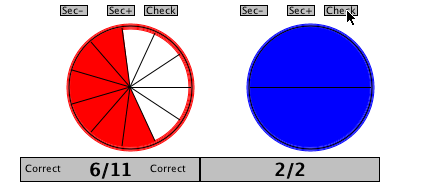
-
If either of your shapes are incorrect, try again. If they are both correct, then place
them in the empty boxes, ordered from lowest to highest. To do this, click in the gray box
below the shape and drag the image into the box.
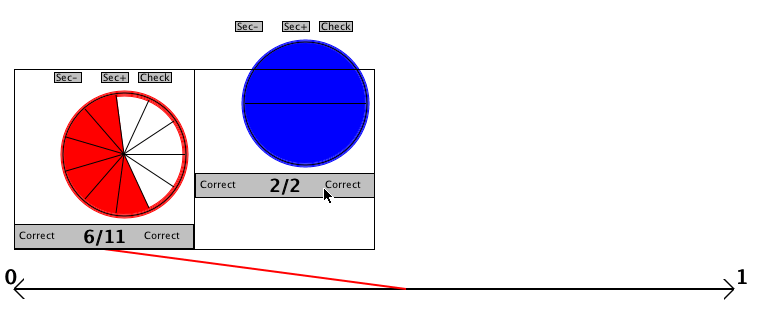
-
Once you believe you have the fractions properly ordered, press the "Check" button to see
if you are right.

- This activity will automatically record how successful you are at answering the questions. To view the score, press the Show Score button at the bottom of the activity and a pop-up window will appear with the scoreboard. The information in this window is divided into two sections. The statistics for the current question are given in the top half of the window, and the statistics for all questions together are given in the bottom half. To close this pop-up window press the Close button or click back on the main window.
- To pause the scoring, press the Active button at the bottom of the screen and it will change to a Paused button. To resume scoring, press the Paused button.
- To reset the scoreboard, open the scoreboard using the Show Score button and then press the Reset button.
Description
This activity allows the user to practice fractions and get a better understanding of them. They get a chance to work with two different aspects of fractions: making them and putting them in order from least to greatest.
This activity would work well in small groups of one or two people. for about 15-20 minutes if you use the exploration questions and 10-15 minutes otherwise.
Place in Mathematics Curriculum
This activity can be used to:
- understand numbers, ways of representing numbers, relationships among numbers, and number systems
- compare and order fractions, decimals and percents efficiently and find their approximatelocations on the number line
- compute fluently and make reasonable estimates
- select appropriate methods and tools for computing with fractions and decimals from among mentalcomputation, estimation, calculators or computers, and paper and pencil, depending on thesituation, and apply the selected methods
- develop and analyze algorithms for computing with fractions, decimals, and integers and developfluency in their use
Standards Addressed
Grade 3
-
Numeration
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of simple fractions with denominators 2, 3, 4, or 10.
Grade 4
-
Numeration
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of fractions with denominators 2 through 12.
Grade 5
-
Numeration
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of positive fractions with denominators 1 through 12 and 100 with proper and mixed numbers and benchmark percents (10%, 25%, 50%, 75%, 100%).
Grade 6
-
Numeration
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of fractions (proper or mixed numbers), decimals, percents (whole number), or integers.
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of fractions, mixed numbers, or percents.
Grade 7
-
Numeration
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of rational numbers (fractions, decimals, percents, or integers).
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of positive fractions, decimals, or percents.
Grade 8
-
Numeration
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of real numbers.
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of rational numbers (fractions, decimals, or percents including integers).
Grade 9
-
Numeration
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of real numbers.
Grade 10
-
Numeration
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of real numbers.
Grade 6
-
Number Sense
- 1.0 Students compare and order positive and negative fractions, decimals, and mixed numbers. Students solve problems involving fractions, ratios, proportions, and percentages
Third Grade
-
Number and Operations-Fractions
- Develop understanding of fractions as numbers.
Fourth Grade
-
Number and Operations-Fractions
- Extend understanding of fraction equivalence and ordering.
- Build fractions from unit fractions by applying and extending previous understandings of operations on whole numbers.
Fifth Grade
-
Number and Operations-Fractions
- Use equivalent fractions as a strategy to add and subtract fractions.
- Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication and division to multiply and divide fractions.
Grades 6-8
-
Numbers and Operations
- Understand meanings of operations and how they relate to one another
Grade 4
-
Number and Operations, Measurement, Geometry, Data Analysis and Probability, Algebra
- COMPETENCY GOAL 1: The learner will read, write, model, and compute with non-negative rational numbers.
Grade 5
-
Number and Operations, Measurement, Geometry, Data Analysis and Probability, Algebra
- COMPETENCY GOAL 1: The learner will understand and compute with non-negative rational numbers.
Grade 6
-
Number and Operations, Measurement, Geometry, Data Analysis and Probability, Algebra
- COMPETENCY GOAL 1: The learner will understand and compute with rational numbers.
Grade 7
-
Number and Operations, Measurement, Geometry, Data Analysis and Probability, Algebra
- COMPETENCY GOAL 1: The learner will understand and compute with rational numbers.
Grade 3
-
Geometry and Spatial Reasoning
- 10. The student recognizes that a line can be used to represent numbers and fractions and their properties and relationships. The student is expected to locate and name points on a number line using whole numbers and fractions, including halves and fourths.
-
Number, Operation, and Quantitative Reasoning
- 2. The student uses fraction names and symbols (with denominators of 12 or less) to describe fractional parts of whole objects or sets of objects.
Grade 4
-
Geometry and Spatial Reasoning
- 10. The student recognizes the connection between numbers and their properties and points on a line. The student is expected to locate and name points on a number line using whole numbers, fractions such as halves and fourths, and decimals such as tenths.
-
Number, Operation, and Quantitative Reasoning
- 2. The student describes and compares fractional parts of whole objects or sets of objects.
Grade 5
-
Number, Operation, and Quantitative Reasoning
- 2. The student uses fractions in problem-solving situations.
3rd Grade
-
Number and Number Sense
- 3.05a The student will divide regions and sets to represent a fraction;
- 3.05b The student will name and write the fractions represented by a given model (area/region, length/measurement, and set). Fractions (including mixed numbers) will include halves, thirds, fourths, eighths, and tenths.
- 3.06 The student will compare the numerical value of two fractions having like and unlike denominators, using concrete or pictorial models involving areas/regions, lengths/measurements, and sets.
7th Grade
-
Computation and Estimation
- 7.4 The student will
- 7.4a The student will solve practical problems using rational numbers (whole numbers, fractions, decimals) and percents
-
Number and Number Sense
- 7.1 The student will compare, order, and determine equivalent relationships between fractions, decimals, and percents, including use of scientific notation for numbers greater than 10.
4th Grade
-
Number and Number Sense
- 4.3
- 4.3 The student will compare the numerical value of fractions (with like and unlike denominators) having denominators of 12 or less, using concrete materials.
8th Grade
-
Computation and Estimation
- 8.3 The student will solve practical problems involving rational numbers, percents, ratios, and proportions. Problems will be of varying complexities and will involve real-life data, such as finding a discount and discount prices and balancing a checkbook.
- 8.3 The student will solve practical problems involving rational numbers, percents, ratios, and proportions. Problems will be of varying complexities and will involve real-life data,
6th Grade
-
Number and Number Sense
- 6.4 The student will compare and order whole numbers, fractions, and decimals, using concrete materials, drawings or pictures, and mathematical symbols.
Secondary
-
Algebra II
- AII.01 The student will identify field properties, axioms of equality and inequality, and properties of order that are valid for the set of real numbers and its subsets, complex numbers, and matrices.
- AII.02 The student will add, subtract, multiply, divide, and simplify rational expressions, including complex fractions.
- AII.03a The student will add, subtract, multiply, divide, and simplify radical expressions containing positive rational numbers and variables and expressions containing rational exponents.
- AII.03b The student will write radical expressions as expressions containing rational exponents and vice versa.
- AII.07 The student will solve equations containing rational expressions and equations containing radical expressions algebraically and graphically. Graphing calculators will be used for solving and for confirming the algebraic solutions.
- AII.1
- AII.2
- AII.3.a
- AII.3.b
- AII.7
Be Prepared to
- give explicit directions on what they are to do. For example "Today we are going to createfractions and then put them in order from least to greatest."
- answer the questions of why and how this will help them.
- discuss different strategies that they can use in making these fractions.
- discuss different strategies that they can use in determing their placement on the number line.