What is Order of Operations Quiz?
This activity allows two users to play a game of order of operations where each player tries to connect four game pieces in a row before his or her opponent does. The players can choose to answer problems which use addition / subtraction, multiplication / division, exponents, and parentheses. They can also choose the difficulty level.
Depending on the order in which the operations are evaluated, answers may be different. To avoid different answers to the same problem the order in which the operations are evaluated must be consistent. Examine the expression
- 3 2 - 5 * 2
For instance, if you square the 3 before negating it, that changes the expression to
- 9 - 5 * 3
whereas if you negate before you square then the expression is
9 - 5 * 3.
The order in which operations are evaluated has been standardized to:
- Parentheses
- Exponents
- Multiplication and Division (from left to right) and where negation is viewed as multiplication by - 1
- Addition and Subtraction (from left to right)
How Do I Use This Activity?
This activity allows the user to practice order of operations with addition/subtraction, multiplication/division, exponents, and parentheses.
In this applet, questions are categorized by a combination of level (which determines the difficulty) and by types of problems listed. For more information on how questions are generated and what each level and problem type means, see Question Types for Order of Operations Quiz and Order of Operations Four.
Controls and Output
-
Before you start the quiz, you can set several options. You can choose how much time you
will have to answer the questions, you can choose the problem difficulty (Whole Numbers
Only, Level 1, Level 2, Level 3), and you can select the types of arithmetic problems you
want to see. Once you have all of the settings as you want them, click the
Start Game button.
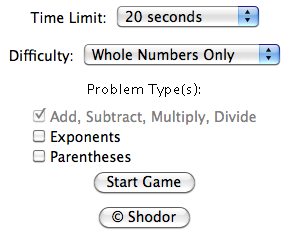 Note that it is impossible to uncheck the "Add, Subtract, Multiply, Divide" box. All
questions will have at least one of these operations.
Note that it is impossible to uncheck the "Add, Subtract, Multiply, Divide" box. All
questions will have at least one of these operations.
-
After clicking the
Start Game button, a new screen appears. On the left, there is a table that lists the types of
questions selected along with the difficulty level.

-
Next, solve the arithmetic problem and enter your answer, rounded to three decimal places
if necessary, into the answer textbox:
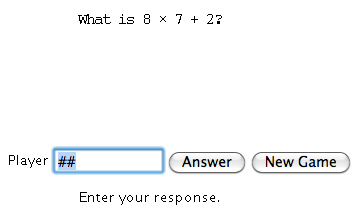
-
After you have entered your answer, you need to click on the
Answer button to find out if you are correct.
-
You have a limited amount of time to answer the question. The
Elapsed Time above the answer textbox shows how much time has elapsed. Once the elapsed time reaches
the amount you set before the game, the time is up.

-
If you want to restart the game, you can do so by clicking on the
New Game button:

-
This activity will automatically record how successful you are at answering the questions.
To view the score, press the
Show Score button at the bottom of the activity and a pop-up window will appear with the scoreboard.
To close this pop-up window press the
Close button or click back on the main window.
-
To pause the scoring, press the
Active button at the bottom of the screen and it will change to a
Paused button. To resume scoring, press the
Paused button.
-
To reset the scoreboard, open the scoreboard using the
Show Score button and then press the
Reset button.
Description
This activity allows a user to practice using the order of operations. The user can choose to answer problems which use addition / subtraction, multiplication / division, exponents, and parentheses. They can also choose the difficulty level. This activity would work well individually for about 15-20 minutes.
Place in Mathematics Curriculum
This activity can be used to:
- Give students practice with basic math skills.
- Develop students mental math skills.
Standards Addressed
Grade 6
-
Estimation and Computation
- The student accurately solves problems (including real-world situations).
-
Numeration
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of fractions (proper or mixed numbers), decimals, percents (whole number), or integers.
Grade 7
-
Estimation and Computation
- The student accurately solves problems (including real-world situations).
Grade 8
-
Estimation and Computation
- The student accurately solves problems (including real-world situations).
Grade 9
-
Estimation and Computation
- The student accurately solves problems (including real-world situations).
-
Numeration
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of real numbers.
Grade 10
-
Estimation and Computation
- The student accurately solves problems (including real-world situations).
-
Numeration
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of real numbers.
Grade 4
-
Number Sense
- 3.0 Students solve problems involving addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division of whole numbers and understand the relationships among the operations
Third Grade
-
Operations and Algebraic Thinking
- Represent and solve problems involving multiplication and division.
- Understand properties of multiplication and the relationship between multiplication and division.
- Multiply and divide within 100.
- Solve problems involving the four operations, and identify and explain patterns in arithmetic.
Fourth Grade
-
Number and Operations in Base Ten
- Use place value understanding and properties of operations to perform multi-digit arithmetic.
-
Operations and Algebraic Thinking
- Use the four operations with whole numbers to solve problems.
Sixth Grade
-
Expressions and Equations
- Apply and extend previous understandings of arithmetic to algebraic expressions.
Eighth Grade
-
Expressions and Equations
- Work with radicals and integer exponents.
Number and Quantity
-
The Real Number System
- Extend the properties of exponents to rational exponents.
Grades 6-8
-
Numbers and Operations
- Understand meanings of operations and how they relate to one another
Grade 6
-
Number and Operations, Measurement, Geometry, Data Analysis and Probability, Algebra
- COMPETENCY GOAL 1: The learner will understand and compute with rational numbers.
Grade 7
-
Number and Operations, Measurement, Geometry, Data Analysis and Probability, Algebra
- COMPETENCY GOAL 1: The learner will understand and compute with rational numbers.
Algebra I
-
Number and Operations
- Competency Goal 1: The learner will perform operations with numbers and expressions to solve problems.
Technical Mathematics I
-
Number and Operations
- Competency Goal 1: The learner will apply various strategies to solve problems.
Integrated Mathematics
-
Number and Operations
- Competency Goal 1: The learner will perform operations with numbers and expressions to solve problems.
6th Grade
-
Numbers and Operations
- The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of the concepts of whole-number percentages, integers, and ratio and rate; the addition and subtraction of fractions; accurate, efficient, and generalizable methods of multiplying and dividing fractions and decimals; and the use of exponential notation to represent whole numbers.
Grade 6
-
Number, Operation, and Quantitative Reasoning
- 2. The student adds, subtracts, multiplies, and divides to solve problems and justify solutions.
Grade 7
-
Number, Operation, and Quantitative Reasoning
- 2. The student adds, subtracts, multiplies, or divides to solve problems and justify solutions.
Grade 8
-
Number, Operation, and Quantitative Reasoning
- 2. The student selects and uses appropriate operations to solve problems and justify solutions.
Textbooks Aligned
Grade Seven
-
Accentuate the Negative
- Investigation Two: Adding Integers
- Investigation Three: Subtracting Integers
- Investigation Four: Multiplying and Dividing Integers
Grade Eight
-
Say It with Symbols
- Investigation One: Order of Operations
Book 1
-
Module 1 - Tools for Success
- Section 4: Order of Operations
-
Module 8 - Our Environment
- Section 1: Adding Integers
- Section 1: Subtracting Integers
Book 2
-
Module 1 - Making Choices
- Section 6: Order of Operations
-
Module 2 - Search and Rescue
- Section 3: Adding Integers
- Section 3: Subtracting Integers
-
Module 3 - A Universal Language
- Section 4: Integer Exponents
-
Module 4 - The Art of Motion
- Section 4: Multiplying Integers
- Section 4: Dividing Integers
- Section 4: Evaluating Expressions
Book 3
-
Module 2 - At the Mall
- Section 4: Operations with Integers
-
Module 3 - The Mystery of Blacktail Canyon
- Section 2: Order of Operations
6th
-
Module 1 - Patterns and Problem Solving
- Section 1: Operations, Estimation, and Mental Math
7th
-
Module 1 - Search and Rescue
- Section 3: Integer Addition and Subtraction
8th
-
Module 2 - At the Mall
- Section 1: Operations with Integers
-
Module 7 - The Algebra Connection
- Section 1: Working with Exponents
Book 1
-
Number Powerhouse
- Lesson 12: Powerhouse Challenge
Book 2
-
Making Mathematical Arguments
- Lesson 1: Statements About Signs
Book 3
-
Exploring the Unknown
- Lesson 4: Lab Problem No. 1
- Lesson 5: Extending the Lab Gear Model
- Lesson 7: Grouping the Ungrouping
Grade 8
-
Reflections on Number
- Multiplication and Division
Grade 6
-
Expressions and Formulas
- Using Order of Operations
-
Operations
- Operations with Integers
Be Prepared to
- Explain how to apply the order of operations.
- Encourage students to try more difficult problems and decrease the allowed time.
- Explain why an exponent takes higher precedence than a negation.
- Explain why negation is considered to be an operator.