What is Transmographer?
This applet allows the user to explore the world of translations, reflections, and rotations. It allows the user to translate triangles, squares, and parallelograms on both the x and y-axes. The user can also reflect the figure around x values, y values, and the line x = y. The applet will also rotate the figure any given number of degrees.
How Do I Use This Activity?
This applet allows the user to explore the world of transformations, reflections, and rotations. It allows the user to translate triangles, squares, and parallelograms on both the x and y-axes.
Controls and Output
-
The user can draw a new triangle, square, or parallelogram on the coordinate plane by
clicking the
New Triangle, New Square, and New parallelogram buttons respectively.

-
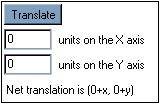
Translate Controls: Clicking and entering a number in the text box beside the phrase
units on the X axis will let the applet know how many units to translate the figure on the X axis. Likewise,
clicking and entering a number in the text box beside the phrase
units on the Y axis will let the applet know how many units to translate the figure on the Y axis. Then
clicking on the
translate button will translate the figure.
-
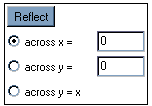
Reflect Controls: Clicking and entering a number in the text box beside the phrase across the X = will let the applet know what vertical line that you want to reflect the figure about. Likewise, clicking and entering a number in the text box beside the phrase across Y = will let the applet know what horizontal line that you want to reflect the figure about. Then clicking on the reflect button will reflect the figure.
Note: By default, the reflection is set to the line X=0, which is equivalent to the Y-axis and the line Y=0, which is equivalent to the X-axis.
-
Rotate Controls: Clicking and entering a number in the text box beside the phrase
degrees will let the applet know how many degrees of rotation you want to use. Then clicking on
the
rotate button will rotate the figure.

- The user may choose to show the position of the original shape by checking the Show Original Polygon check box. When this box is checked the position of the initial polygon is outlined in blue.
- The user may also choose to show the positioning of the last polygon displayed on the screen by checking the Show Pre-image check box. When this box is checked a grey outline is shown at the position where the shape was located prior to the last transformation, reflection, or rotation.
Description
This activity allows the user to experiment with translation, reflection and rotation in the Cartesian coordinate plane. This activity would work well in mixed ability groups of two or four for about forty-five minutes if you use the exploration questions or the worksheet and fifteen to twenty minutes otherwise. If you wish to use both supplements, this activity will take approximately sixty minutes.
Place in Mathematics Curriculum
This activity can be used to:
- Illustrate plotting basic shapes on the Cartesian coordinate system
- Develop students mental visualization skills
- Introduce the ideas of translation, reflection and rotation
- Practice students skills at translation, reflection and rotation
Standards Addressed
Grade 3
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of similarity, congruence, symmetry, or transformations of shapes.
- The student demonstrates understanding of position and direction.
- The student demonstrates a conceptual understanding of geometric drawings or constructions.
Grade 4
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of similarity, congruence, symmetry, or transformations of shapes.
- The student demonstrates understanding of position and direction.
- The student demonstrates a conceptual understanding of geometric drawings or constructions.
Grade 5
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of similarity, congruence, symmetry, or transformations of shapes.
- The student demonstrates understanding of position and direction.
- The student demonstrates a conceptual understanding of geometric drawings or constructions.
Grade 6
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of similarity, congruence, symmetry, or transformations of shapes.
- The student solves problems (including real-world situations) using perimeter, area, or volume.
- The student demonstrates understanding of position and direction.
Grade 7
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of similarity, congruence, symmetry, or transformations of shapes.
- The student solves problems (including real-world situations).
- The student demonstrates understanding of position and direction.
Grade 8
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of similarity, congruence, symmetry, or transformations of shapes.
- The student solves problems (including real-world situations).
- The student demonstrates understanding of position and direction.
Grade 9
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates an understanding of geometric relationships.
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of similarity, congruence, symmetry, or transformations of shapes.
- The student demonstrates understanding of position and direction when solving problems (including real-world situations).
- The student demonstrates a conceptual understanding of geometric drawings or constructions.
Grade 10
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates an understanding of geometric relationships.
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of similarity, congruence, symmetry, or transformations of shapes.
- The student demonstrates understanding of position and direction when solving problems (including real-world situations).
- The student demonstrates a conceptual understanding of geometric drawings or constructions.
Eighth Grade
-
Geometry
- Understand congruence and similarity using physical models, trans- parencies, or geometry software.
Geometry
-
Congruence
- Experiment with transformations in the plane
- Understand congruence in terms of rigid motions
Grades 6-8
-
Geometry
- Apply transformations and use symmetry to analyze mathematical situations
- Specify locations and describe spatial relationships using coordinate geometry and other representational systems
Grades 9-12
-
Geometry
- Apply transformations and use symmetry to analyze mathematical situations
Grade 6
-
Number and Operations, Measurement, Geometry, Data Analysis and Probability, Algebra
- COMPETENCY GOAL 3: The learner will understand and use properties and relationships of geometric figures in the coordinate plane.
Geometry
-
Data Analysis and Probability
- Competency Goal 3: The learner will transform geometric figures in the coordinate plane algebraically.
Technical Mathematics I
-
Algebra
- Competency Goal 3: The learner will describe the transformation of polygons in the coordinate plane algebraically.
Pre-Calculus
-
Number and Operations
- Competency Goal 1: The learner will describe geometric figures in the coordinate plane algebraically.
Integrated Mathematics II
-
Geometry and Measurement
- Competency Goal 2: The learner will describe geometric figures in the coordinate plane algebraically.
3rd Grade
-
Geometry
- The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of the connection between the identification of basic attributes and the classification of two-dimensional shapes.
6th Grade
-
Geometry
- The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of shape, location, and movement within a coordinate system; similarity, complementary, and supplementary angles; and the relationship between line and rotational symmetry.
5th Grade
-
Geometry
- The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of congruency, spatial relationships, and relationships among the properties of quadrilaterals.
4th Grade
-
Geometry
- Standard 4-4: The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of the relationship between two- and three-dimensional shapes, the use of transformations to determine congruency, and the representation of location and moveme
- Standard 4-4: The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of the relationship between two- and three-dimensional shapes, the use of transformations to determine congruency, and the representation of location and movement within the first quadrant of a coordinate system.
7th Grade
-
Geometry
- The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of proportional reasoning, tessellations, the use of geometric properties to make deductive arguments. the results of the intersection of geometric shapes in a plane, and the
Intermediate Algebra
-
Algebra
- The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of functions, systems of equations, and systems of linear inequalities.
5th Grade
-
Geometry
- The student will develop an understanding of geometric concepts and relationships as the basis for geometric modeling and reasoning to solve problems involving one-, two-, and three-dimensional figures.
3rd Grade
-
Geometry
- Content Standard 3.0 The student will develop an understanding of geometric concepts and relationships as the basis for geometric modeling and reasoning to solve problems involving one-, two-, and three-dimensional figures.
4th Grade
-
Geometry
- The student will develop an understanding of geometric concepts and relationships as the basis for geometric modeling and reasoning to solve problems involving one-, two-, and three-dimensional figures.
Grade 4
-
Geometry and Spatial Reasoning
- 9. The student connects transformations to congruence and symmetry.
Grade 5
-
Geometry and Spatial Reasoning
- 8. The student models transformations.
Grade 8
-
Geometry and Spatial Reasoning
- 6. The student uses transformational geometry to develop spatial sense.
7th Grade
-
Geometry
- 7.13 The student, given a polygon in the coordinate plane, will represent transformations — rotation and translation — by graphing the coordinates of the vertices of the transformed polygon and sketching the resulting figure.
4th Grade
-
Geometry
- 4.17.c The student will investigate congruence of plane figures after geometric transformations such as reflection (flip), translation (slide) and rotation (turn), using mirrors, paper folding, and tracing.
-
Geomety
- 4.17.c
5th Grade
-
Geometry
- 5.15a The student, using two-dimensional (plane) figures (square, rectangle, triangle, parallelogram, rhombus, kite, and trapezoid) will recognize, identify, describe, and analyze their properties in order to develop definitions of these figures
- 5.15d The student, using two-dimensional (plane) figures (square, rectangle, triangle, parallelogram, rhombus, kite, and trapezoid) will identify and describe a line of symmetry
8th Grade
-
Geometry
- 8.8 The student will apply transformations (rotate or turn, reflect or flip, translate or slide, and dilate or scale) to geometric figures represented on graph paper. The student will identify applications of transformations, such as tiling, fabric design, art, and scaling.
- 8.8 The student will apply transformations (rotate or turn, reflect or flip, translate or slide,
Textbooks Aligned
Grade Six
-
Ruins of Montarek
- Investigation One: Building Plans
Grade Eight
-
Kaleidoscopes, Hubcaps, and Mirrors
- Investigation One: Three Types of Symmetry
- Investigation Two: Symmetry Transformations
- Investigation Three: Transforming Coordinates
- Investigation Four: Symmetry and Algebra
6th
-
Module 8 - MATH-Thematical Mix
- Section 5: Transformations
7th
-
Module 4 - The Art of Motion
- Section 4: Rotations and Reflections
- Section 6: Translations, Similarity, and Two-Step Equations
8th
-
Module 6 - Visualizing Change
- Section 4: Algorithms and Transformations
Book 1
-
Designing Spaces
- Lesson 2: Seeing Around the Corners
Book 2
-
Getting In Shape
- Lesson 4: Tiling with Triangles
Grade 5
-
Figuring All the Angles
- Measuring Angles
- Rectangular Coordinates
-
Side Seeing
- Relationship between three dimensional shapes and two dimensional drawings
Grade 7
-
Triangles and Beyond
- Relationships between sides and angles of a triangle
- Parallel Lines
- Constructing Triangles
- Transformations
- Congruence
- Similarity
Be Prepared to
- Define translation, reflection, and rotation and show examples
- Explain net translation and net rotation