What is Algebra Four?
This activity allows the user to practice solving algebraic equations.
This activity is similar to Connect Four, and is designed for two players. The goal is to have four pieces of the same color connected either horizontally, vertically, or diagonally. One player uses red pieces, while the other player uses blue pieces. To earn a piece, you need to correctly solve an algebraic equation.
Solving an algebraic equation means finding the value of an unknown value in an equation that makes that equation true. For equations in the Algebra Four activity, you will be asked to find solutions to single variable equations.
There are many ways to solve algebraic equations. Frequently, solving algebraic equations entails "isolating the variable" using relationships of equality and properties of real numbers such as the distributive property, the associative property, the commutative property and both multiplicative inverses and additive inverses.
Quadratic equations are also found in the Algebra Four game. An equation is considered "quadratic" when the variable is squared, such as x 2 =25. This type of equation often has two different answers that make the equation true, such as this one, x can be +5 or -5.
How Do I Use This Activity?
This activity allows the user to practice solving linear and quadratic algebraic equations.
In this applet, questions are categorized by a combination of level (which determines the difficulty) and by types of problems listed. For more information on how questions are generated and what each level and problem type means, see Question Types for Algebra Quiz and Algebra Four.
Controls and Output
- This activity is similar to Connect Four, and is designed for two players. The goal is to have four pieces of the same color connected either horizontally, vertically, or diagonally. One player uses red pieces, while the other player uses black pieces.
-
Before you start the game, you can set several options. You can choose how much time each player will have to answer the questions, you can choose the problem difficulty (Level 1, Level 2, Level 3, or Whole Numbers Only) and you can select the types of algebra problems you want to see. Once you have all of the settings as you want them, click the Start Game button.
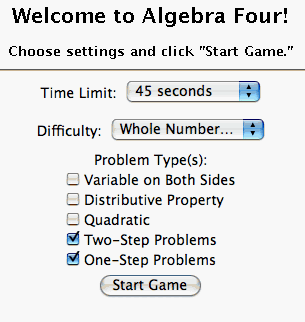
*Note that the Whole Numbers Only questions are the same types of questions used in Level 1 but all numbers in the equation (as well the answer) will be positive integers. Most Level 1 solutions have integer answers, Level 2 problems tend to have integers in the problem but may have fractional solutions, and Level 3 tends to have fractions in the problem and in the solution.
-
After clicking the
Start Game button, a new screen appears. Towards the left of the screen is a table that lists the
types of questions selected along with the difficulty level.

-
To earn a piece you need to solve an algebraic equation, enter your answer into the answer
textbox, and click the
Answer button.
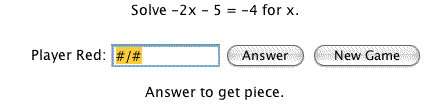
- Note that for fractions you must enter your answer with a '/' symbol in between the numerator and denominator: as #/#. For quadratics with two solutions, enter your answer with a comma in between the two solutions: #,#. For quadratics with a single solution, you must enter the number only once for your answer.
-
The
timer on the right-hand side of the board shows how much time you have left to answer. Once the
timer turns all gray, the time is up. If you chose "No Time Limit," the timer will simply
be gray, and it will not count down.

-
If a player answers a question correctly, the player will be able to place one of their
pieces on the board. To place a piece, simply click on the column that you want to drop
the piece into.
The piece will fall into the lowest available slot in the column. If a player answers incorrectly or if time runs out, the other player will have a chance
to answer. If neither player is correct the answer appears in a pop-up window.
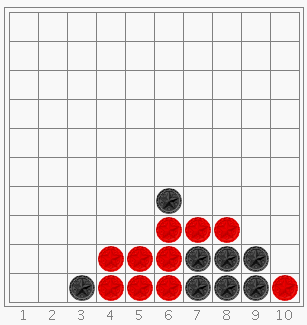
- If a player -- Player Red for instance -- answers incorrectly, the other player -- Player Black -- will be asked to answer the question. If Black also answers incorrectly, the answer will be displayed in a pop-up window and the game will continue with a new question for Black. Note that whether or not player Black answers correctly, it will be Black's turn again, because Black just attempted Red's question.
-
If you want to restart the game or change options selected on the beginning screen, you
can do so by clicking on the
New Game button:
-
The user may change the font size at any time during the game by selecting one of the
three radio buttons located on the left side of the screen.
Scoring
-
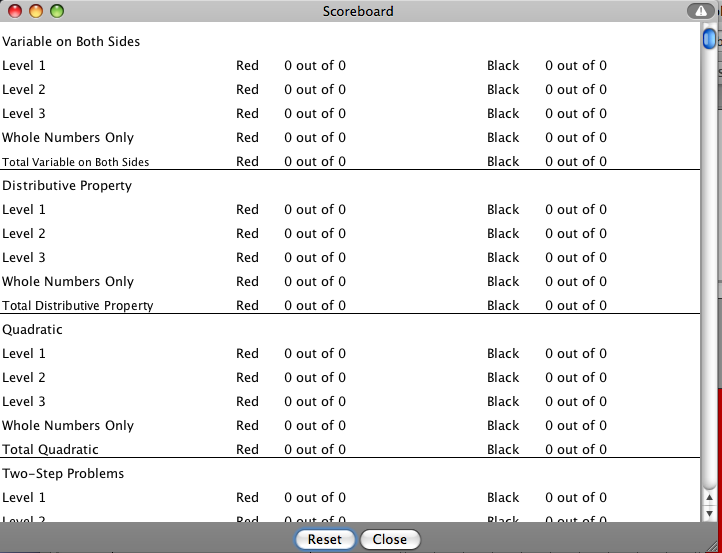
This activity will automatically record how successful you are at answering the questions.
To view the score, press the
Show Score button at the bottom of the activity and a pop-up window will appear with the scoreboard.
- To close this pop-up window press the Close button or click back on the main window.
- To pause the scoring, press the Active button at the bottom of the screen and it will change to a Paused button. To resume scoring, press the Paused button.
- To reset the scoreboard, open the scoreboard using the Show Score button and then press the Reset button.
Description
This activity allows the user to play a game with solving equations where each player tries to connect four game pieces in a row before his or her opponent does. The players can choose to solve linear equations involving various properties of equality as well as solve quadratic equations in standard form. They can also choose the difficulty level and the number of players. This activity would work well in groups of 2 for about 25-30 minutes if you use the exploration questions and 15-20 minutes otherwise.
Place in Mathematics Curriculum
This activity can be used to:
- Allow students practice with solving various types of one-variable equations.
Standards Addressed
Grade 6
-
Functions and Relationships
- The student demonstrates algebraic thinking.
-
Numeration
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of fractions (proper or mixed numbers), decimals, percents (whole number), or integers.
Grade 7
-
Functions and Relationships
- The student demonstrates algebraic thinking.
Grade 8
-
Functions and Relationships
- The student demonstrates algebraic thinking.
Grade 9
-
Functions and Relationships
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of functions, patterns, or sequences including those represented in real-world situations.
- The student demonstrates algebraic thinking.
Grade 10
-
Functions and Relationships
- The student demonstrates conceptual understanding of functions, patterns, or sequences including those represented in real-world situations.
- The student demonstrates algebraic thinking.
Grade 6
-
Algebra and Functions
- 1.0 Students write verbal expressions and sentences as algebraic expressions and equations; they evaluate algebraic expressions, solve simple linear equations, and graph and interpret their results
Grade 7
-
Algebra and Functions
- 1.0 Students express quantitative relationships by using algebraic terminology, expressions, equations, inequalities, and graphs
- 3.0 Students graph and interpret linear and some nonlinear functions
- 4.0 Students solve simple linear equations and inequalities over the rational numbers
Sixth Grade
-
Expressions and Equations
- Apply and extend previous understandings of arithmetic to algebraic expressions.
- Reason about and solve one-variable equations and inequalities.
- Represent and analyze quantitative relationships between dependent and independent variables.
Seventh Grade
-
Expressions and Equations
- Solve real-life and mathematical problems using numerical and algebraic expressions and equations.
Algebra
-
Arithmetic with Polynomials and Rational Expressions
- Perform arithmetic operations on polynomials
- Understand the relationship between zeros and factors of polynomials
- Rewrite rational expressions
-
Reasoning with Equations and Inequalities
- Understand solving equations as a process of reasoning and explain the reasoning
- Solve equations and inequalities in one variable
-
Seeing Structure in Expressions
- Write expressions in equivalent forms to solve problems
Grades 6-8
-
Algebra
- Represent and analyze mathematical situations and structures using algebraic symbols
Grade 5
-
Number and Operations, Measurement, Geometry, Data Analysis and Probability, Algebra
- COMPETENCY GOAL 5: The learner will demonstrate an understanding of patterns, relationships, and elementary algebraic representation.
Grade 6
-
Number and Operations, Measurement, Geometry, Data Analysis and Probability, Algebra
- COMPETENCY GOAL 5: The learner will demonstrate an understanding of simple algebraic expressions.
Grade 7
-
Number and Operations, Measurement, Geometry, Data Analysis and Probability, Algebra
- COMPETENCY GOAL 5: The learner will demonstrate an understanding of linear relations and fundamental algebraic concepts.
Algebra I
-
Number and Operations
- Competency Goal 1: The learner will perform operations with numbers and expressions to solve problems.
Integrated Mathematics
-
Number and Operations
- Competency Goal 1: The learner will perform operations with numbers and expressions to solve problems.
Integrated Mathematics II
-
Number and Operations
- Competency Goal 1: The learner will perform operations with numbers, algebraic expressions, and matrices to solve problems.
Grade 7
-
Patterns, Relationships, and Algebraic Thinking
- 5. The student uses equations to solve problems.
Algebra I
-
Foundation for Functions
- 2. The student uses the properties and attributes of functions.
- 4. The student understands the importance of the skills required to manipulate symbols in order to solve problems and uses the necessary algebraic skills required to simplify algebraic expressions and solve equations and inequalities in problem situations.
-
Linear Functions
- 7. The student formulates equations and inequalities based on linear functions, uses a variety of methods to solve them, and analyzes the solutions in terms of the situation.
- 8. The student formulates systems of linear equations from problem situations, uses a variety of methods to solve them, and analyzes the solutions in terms of the situation.
-
Quadratic and Other Nonlinear Functions
- 10. The student understands there is more than one way to solve a quadratic equation and solves them using appropriate methods.
Secondary
-
Algebra I
- A.01 The student will solve multistep linear equations and inequalities in one variable, solve literal equations (formulas) for a given variable, and apply these skills to solve practical problems. Graphing calculators will be used to confirm algebraic solutions.
- A.14 The student will solve quadratic equations in one variable both algebraically and graphically. Graphing calculators will be used both as a primary tool in solving problems and to verify algebraic solutions.
Textbooks Aligned
Grade Seven
-
Moving Straight Ahead
- Investigation Four: Solving Equations
Grade Eight
-
Say It with Symbols
- Investigation Four: Solving Equations
Book 2
-
Module 2 - Search and Rescue
- Section 5: Using Inverse Operations for Addition and Subtraction
-
Module 3 - A Universal Language
- Section 6: Constructing Triangles
- Section 6: Multiplication and Division Equations
-
Module 4 - The Art of Motion
- Section 5: Translations
- Section 5: Solving 2-Step Equations
Book 3
-
Module 1 - Amazing Feats, Facts and Fictions
- Section 4: Finding Circumferences
- Section 4: Finding Volumes
- Section 5: Writing Equations
7th
-
Module 2 - Bright Ideas
- Section 1: Decimals and Exponents
8th
-
Module 1 - Amazing Feats and Facts and Fiction
- Section 3: Equations and Expressions
-
Module 3 - The Mystery of Blacktail Canyon
- Section 1: Square Roots and Measurement
-
Module 6 - Visualizing Change
- Section 2: Linear Equations and Problem Solving
Book 2
-
The Language of Algebra
- Lesson 10: Solving Simple Equations and Inequalities
- Lesson 11: The Balancing Act
Book 3
-
Exploring the Unknown
- Lesson 7: Grouping the Ungrouping
- Lesson 10: Simplify and Solve
Be Prepared to
- Explain the difference between solving a quadratic equation vs. solving a linear one
- Encourage students to try more difficult problems and decrease the allowed time
- Prevent any disputes and taunting between winners and losers