What is Generalized Monty Hall?
This activity allows the user to experiment with conditional probability by choosing to stay or to switch doors. This applet also allows the user to control the number of doors to increase or decrease the probability of finding the right door.
Conditional probability is the probability that an event will occur based on the outcome of the previous event. The condition in this game is that the first move opens one of the other 2 doors and shows the user that the prize is not behind that door. Based on the information the user just learned he has a better chance of guessing the correct door.
Probability began in the middle of the seventeenth century by a man named Pascal. One day a man proposed a question about gambling. His question was "If I play a game that I have eight rolls to roll a six and I fail the first three times, how much of my bet should I get back?" The game involved chance just as most games do now, such as Monopoly and card games. Las Vegas is a city that is dominated by people that have invested in this field of mathematics. Today, probability has found its way into the fields of science, medicine, and statistics.
How Do I Use This Activity?
This activity allows the user to simulate the Monty Hall Game with up to 100 doors in which the user chooses a door, and then all but one door is opened to reveal a stinking pig. The player must then decide to stick with the original choice or change.
Controls and Output
-
To select the number of doors, type the desired number in the
Number of Doors = [___] space. Here the number of doors is 3:
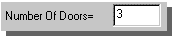
-
To select the number of games simulated, type the desired number in the
Number of Trials = [___] space. Here the number of trials is 1000:

-
To select whether the player switches the doors or stays with the original choice, click
on the selection sign:
Stay
 Stay or Switch. Here Stay is selected:
Stay or Switch. Here Stay is selected:

-
To run the simulation, click on the
Run Simulation button:

-
Observe the total number of prizes the player obtained in all the games in
The number of prizes: [___] space. Here the number of prizes is 316:

Description
This activity allows the user to simulate the Monty Hall Game with up to 100 doors in which the user chooses a door, and then all but one door is opened to reveal a stinking pig. The player must then decide to stick with the original choice or change. This activity would work well in groups of two to four for about twenty to twenty-five minutes if you use the exploration questions and five minutes otherwise.
Place in Mathematics Curriculum
This activity can be used to:
- introduce the notions of chance and probability
- motivate the notion of conditional probability
- motivate the notion of random numbers
Standards Addressed
Grade 6
-
Statistics and Probability
- The student demonstrates a conceptual understanding of probability and counting techniques.
Grade 7
-
Statistics and Probability
- The student demonstrates a conceptual understanding of probability and counting techniques.
Grade 8
-
Statistics and Probability
- The student demonstrates a conceptual understanding of probability and counting techniques.
Grade 9
-
Statistics and Probability
- The student demonstrates a conceptual understanding of probability and counting techniques.
Grade 10
-
Statistics and Probability
- The student demonstrates a conceptual understanding of probability and counting techniques.
Grades 8-12
-
Probability and Statistics
- 1.0 Students know the definition of the notion of independent events and can use the rules for addition, multiplication, and complementation to solve for probabilities of particular events in finite sample spaces.
Seventh Grade
-
Statistics and Probability
- Investigate chance processes and develop, use, and evaluate probability models.
Statistics and Probability
-
Conditional Probability and the Rules of Probability
- Understand independence and conditional probability and use them to interpret data
- Use the rules of probability to compute probabilities of compound events in a uniform probability model
-
Making Inferences and Justifying Conclusions
- Understand and evaluate random processes underlying statistical experiments
- Make inferences and justify conclusions from sample surveys, experiments, and observational studies
-
Using Probability to Make Decisions
- Calculate expected values and use them to solve problems
- Use probability to evaluate outcomes of decisions
Grades 6-8
-
Data Analysis and Probability
- Develop and evaluate inferences and predictions that are based on data
Grades 9-12
-
Data Analysis and Probability
- Develop and evaluate inferences and predictions that are based on data
- Formulate questions that can be addressed with data and collect, organize, and display relevant data to answer them
- Understand and apply basic concepts of probability
AP Statistics
-
Data Analysis and Probability
- Competency Goal 3: The learner will collect and analyze data to solve problems.
-
Number and Operations
- Competency Goal 1: The learner will analyze univariate data to solve problems.
6th Grade
-
Data Analysis & Probability
- Content Standard 5.0 The student will understand and apply basic statistical and probability concepts in order to organize and analyze data and to make predictions and conjectures.
7th Grade
-
Data Analysis & Probability
- The student will understand and apply basic statistical and probability concepts in order to organize and analyze data and to make predictions and conjectures.
8th Grade
-
Data Analysis & Probability
- The student will understand and apply basic statistical and probability concepts in order to organize and analyze data and to make predictions and conjectures.
7th Grade
-
Probability and Statistics
- 7.18 The student will make inferences, conjectures, and predictions based on analysis of a set of data.
8th Grade
-
Probability and Statistics
- 8.11 The student will analyze problem situations, including games of chance, board games, or grading scales, and make predictions, using knowledge of probability.
Secondary
-
Probability and Statistics
- PS.12 The student will identify and describe two or more events as complementary, dependent, independent, and/or mutually exclusive.
- PS.13 The student will find probabilities (relative frequency and theoretical), including conditional probabilities for events that are either dependent or independent, by applying the "law of large numbers" concept, the addition rule, and the multiplication rule.
Be Prepared to
- answer the question "What is Monty Hall?"
- discuss probability and conditional probability