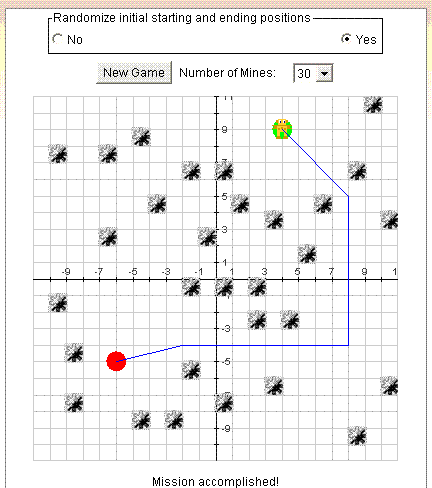
What is Maze Game?
This activity allows the user to practice their point plotting skills by having them move a robot through a mine field to a target location. Moves are accomplished by specifying the coordinates of the new location. In order to win, the path must not cross a mine.
The coordinate plane system was developed by a sick mathematician. As Rene Descarte lay in bed sick, he saw a fly buzzing around on the ceiling. His ceiling was made of square tiles. As he watched, he realized that he could describe the position of the fly by the ceiling tile he was on. After this experience, he developed the Cartesian coordinate system in the 17th century to help visualize functions via plotting function values as ordered pairs. In this system a grid of evenly spaced horizontal and vertical lines is drawn, a center or "origin" is chosen, and horizontal and vertical scales are chosen. Here's an example:
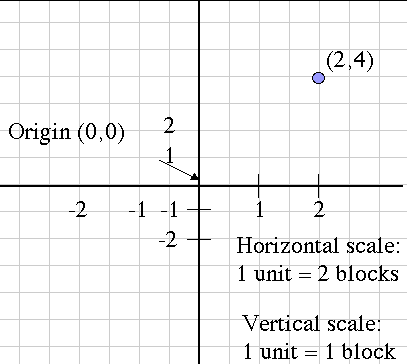
Notice that the blue point is labeled with its Cartesian coordinates, the horizontal and vertical movement from the origin, in that order. This is the mathematical convention for naming points.
Another name for the horizontal movement value is the abscissa, and the vertical movement is the ordinate. These terms are more rare now than they used to be, but you might still hear them being used.
How Do I Use This Activity?
This activity allows the user to practice their point plotting skills by having them move a robot through a mine field to a target location.
Controls and Output
-
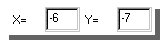
Determine the X and Y coordinates at the end point of the robot's next step. For example,
we want the robot to go to the point highlighted by a yellow dot. The X coordinate of the
point is -6, and the Y coordinate of the point is -7:

-
To command the robot to make the next step, type the X coordinate in the
X=[___] space, and the Y coordinate in the
Y=[___] space:
-
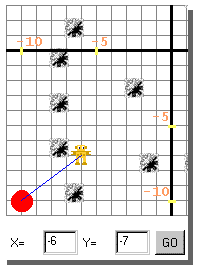
When coordinates for the next step are prepared, click on the
GO button to make the robot move. The movements of the robot are traced in blue as long as
the robot does not come in contact with any mines.
-
If the robot comes in contact with a mine along his journey, the movements of the robot
are then traced in red.
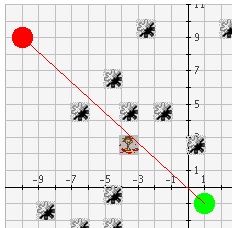
-
To start a new game, choose the Number of Mines you want on the board:
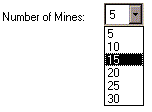 and click on the
New Game button:
and click on the
New Game button:

-
The user may control whether the robot starting and target positions are fixed or variable using the following control:
If this control is set to No, the robot's starting position is always (-10, -10) and the robot's target position is always (10, 10). If this control is set to Yes, the robot's starting and target position are placed at random positions on the screen as shown below:
Scoring
-
This activity will automatically record how successful you are at answering the questions.
To view the score, press the
Show Score button at the bottom of the activity and a pop-up window will appear with the scoreboard.
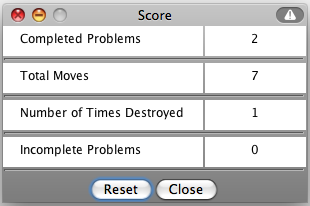
- To close this pop-up window press the Close button or click back on the main window.
- To pause the scoring, press the Active button at the bottom of the screen and it will change to a Paused button. To resume scoring, press the Paused button.
- To reset the scoreboard, open the scoreboard using the Show Score button and then press the Reset button.
Because this activity randomly generates questions, a feature called Seed Random has been implemented that allows multiple users using different computers to work on the same problem. See Seed Random Help for instructions on using this feature.
Description
This activity allows the user to practice their point plotting skills by having them move a robot through a mine field to a target location. Moves are accomplished by specifying the coordinates of the new location. In order to win, the path must not cross a mine. This activity would work well in groups of two for about thirty minutes if you use the exploration questions and fifteen minutes otherwise.
Place in Mathematics Curriculum
This activity can be used to:
- introduce the Cartesian coordinate system
- practice students' point plotting skills
- practice students' graph reading skills
- motivate the concept of slope
Standards Addressed
Grade 3
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates understanding of position and direction.
Grade 4
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates understanding of position and direction.
Grade 5
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates understanding of position and direction.
Grade 6
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates understanding of position and direction.
Grade 7
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates understanding of position and direction.
Grade 8
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates understanding of position and direction.
Grade 9
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates understanding of position and direction when solving problems (including real-world situations).
Grade 10
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates understanding of position and direction when solving problems (including real-world situations).
Fifth Grade
-
Geometry
- Graph points on the coordinate plane to solve real-world and mathematical problems.
Grade 6
-
Number and Operations, Measurement, Geometry, Data Analysis and Probability, Algebra
- COMPETENCY GOAL 3: The learner will understand and use properties and relationships of geometric figures in the coordinate plane.
Grade 7
-
Number and Operations, Measurement, Geometry, Data Analysis and Probability, Algebra
- COMPETENCY GOAL 5: The learner will demonstrate an understanding of linear relations and fundamental algebraic concepts.
Textbooks Aligned
Grade Six
-
Data About Us
- Investigation Four: Coordinate Graphs
Book 1
-
Module 7 - Wonders of the World
- Section 6: Temperature and Integers
- Section 6: Graphing Ordered Pairs
Book 2
-
Module 2 - Search and Rescue
- Section 2: Comparing Integers
- Section 2: Coordinate Graphing of Integers
6th
-
Module 7 - Wonders of the World
- Section 5: Temperature, Integers, and Coordinate Graphs
7th
-
Module 1 - Search and Rescue
- Section 2: Integers and Coordinates
Be Prepared to
- answer the question "How do you find distance?"
- discuss distance, positive and negative coordinates, quadrants, etc