What is Simple Coordinates Game?
This activity allows the user to plot points on the coordinate plane and to read the coordinates of a point plotted by the computer.
The Cartesian coordinate system was formalized by Rene Descartes in the 17th century to help visualize functions via plotting function values as ordered pairs. In this system a grid of evenly spaced horizontal and vertical lines are drawn, a center or "origin" is chosen, and horizontal and vertical scales are chosen. Here's an example:
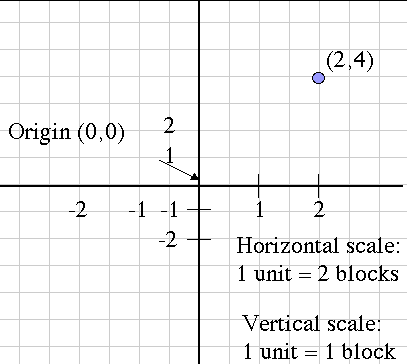
Notice that the horizontal and vertical scales are different, but each one considered alone is evenly spaced. Also, the blue point is labeled with its Cartesian coordinates, the horizontal and vertical movement from the origin, in that order. This is the mathematical convention for naming points.
Another name for the horizontal movement value is the abscissa, and the vertical movement is the ordinate. These terms are more rare now than they used to be, but you might still hear them being used.
How Do I Use This Activity?
This activity allows the user to plot points on the coordinate plane and to read the coordinates of a point plotted by the computer.
Controls and Output
This game can be played in two different ways:
Game 1: When you input an "address" (i.e., coordinates), a house is drawn at the point with these coordinates.
-
Type the coordinates of the grid line intersection where you want to place the house in
the
X=[___] and
Y=[___] spaces (here X=4 and Y=3):
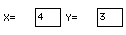
-
Click on the
Plot button to have software draw the house:
-
Click on the
New Point button to obtain a house with a new address:

-
Determine X and Y coordinates of the house. Here X=4 and Y=3:
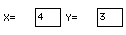
-
To have the software check your coordinates:
-
type the coordinates in the
X=[___] and
Y=[___] spaces:
-
click on the
Check button:

-
type the coordinates in the
X=[___] and
Y=[___] spaces:
-
Click on the
New Point button to obtain a house with a new address:

Scoring
- This activity will automatically record how successful you are at answering the questions. To view the score, press the Show Score button at the bottom of the activity and a pop-up window will appear with the scoreboard. To close this pop-up window press the Close button or click back on the main window.
- To pause the scoring, press the Active button at the bottom of the screen and it will change to a Paused button. To resume scoring, press the Paused button.
- To reset the scoreboard, open the scoreboard using the Show Score button and then press the Reset button.
Because this activity randomly generates questions, a feature called Seed Random has been implemented that allows multiple users using different computers to work on the same problem. See Seed Random Help for instructions on using this feature.
Description
This activity allows the user to plot points on the coordinate plane and to read the coordinates of a point plotted by the computer. This activity would work well in groups of two or three for about fifteen to twenty minutes if you use the exploration questions and ten to fifteen minutes otherwise.
Place in Mathematics Curriculum
This activity can be used to:
- introduce the Cartesian coordinate system
- practice students' point plotting skills
- practice students' graph reading skills
Standards Addressed
Grade 3
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates understanding of position and direction.
Grade 4
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates understanding of position and direction.
Grade 5
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates understanding of position and direction.
Grade 6
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates understanding of position and direction.
Grade 7
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates understanding of position and direction.
Grade 8
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates understanding of position and direction.
Grade 9
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates understanding of position and direction when solving problems (including real-world situations).
Grade 10
-
Geometry
- The student demonstrates understanding of position and direction when solving problems (including real-world situations).
Grade 4
-
Measurement and Geometry
- 2.0 Students use two-dimensional coordinate grids to represent points and graph lines and simple figures
Fifth Grade
-
Geometry
- Graph points on the coordinate plane to solve real-world and mathematical problems.
Grades 3-5
-
Geometry
- Specify locations and describe spatial relationships using coordinate geometry and other representational systems
Grade 4
-
Number and Operations, Measurement, Geometry, Data Analysis and Probability, Algebra
- COMPETENCY GOAL 3: The learner will recognize and use geometric properties and relationships.
Grade 6
-
Number and Operations, Measurement, Geometry, Data Analysis and Probability, Algebra
- COMPETENCY GOAL 3: The learner will understand and use properties and relationships of geometric figures in the coordinate plane.
Grade 7
-
Number and Operations, Measurement, Geometry, Data Analysis and Probability, Algebra
- COMPETENCY GOAL 5: The learner will demonstrate an understanding of linear relations and fundamental algebraic concepts.
6th Grade
-
Geometry
- The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of shape, location, and movement within a coordinate system; similarity, complementary, and supplementary angles; and the relationship between line and rotational symmetry.
4th Grade
-
Geometry
- Standard 4-4: The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of the relationship between two- and three-dimensional shapes, the use of transformations to determine congruency, and the representation of location and moveme
- Standard 4-4: The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of the relationship between two- and three-dimensional shapes, the use of transformations to determine congruency, and the representation of location and movement within the first quadrant of a coordinate system.
Elementary Algebra
-
Elementary Algebra
- Standard EA-4: The student will demonstrate through the mathematical processes an understanding of the procedures for writing and solving linear equations and inequalities.
5th Grade
-
Geometry
- The student will develop an understanding of geometric concepts and relationships as the basis for geometric modeling and reasoning to solve problems involving one-, two-, and three-dimensional figures.
4th Grade
-
Geometry
- The student will develop an understanding of geometric concepts and relationships as the basis for geometric modeling and reasoning to solve problems involving one-, two-, and three-dimensional figures.
Grade 5
-
Geometry and Spatial Reasoning
- 9. The student recognizes the connection between ordered pairs of numbers and locations of points on a plane. The student is expected to locate and name points on a coordinate grid using ordered pairs of whole numbers.
Grade 6
-
Geometry and Spatial Reasoning
- 7. The student uses coordinate geometry to identify location in two dimensions. The student is expected to locate and name points on a coordinate plane using ordered pairs of non-negative rational numbers.
Grade 7
-
Geometry and Spatial Reasoning
- 7. The student uses coordinate geometry to describe location on a plane.
4th Grade
-
Geometry
- 4.18 The student will identify the ordered pair for a point and locate the point for an ordered pair in the first quadrant of a coordinate plane.
-
Geomety
- 4.18
Textbooks Aligned
Book 1
-
Module 4 - Mind Games
- Section 5: Graphing on the Coordinate Grid
- Section 5: Expressions and Equations Multiples
Be Prepared to
- answer the question "Which is X and which is Y?"
- discuss positive and negative coordinate, quadrants, etc.